Activity problem. Citric acid is a triprotic acid (H 3 A) whose anion (A 3- ) forms
Question:
Activity problem. Citric acid is a triprotic acid (H3A) whose anion (A3-) forms stable complexes with many metal ions.
When a Ca2+ ion-selective electrode with a slope of 29.58 mV was immersed in a solution having ACa2+ = 1.00 × 10-3 , the reading was +2.06 mV. Calcium citrate solution was prepared by mixing equal volumes of solutions 1 and 2.
Solution 1:
[Ca2+] = 1.00 × 10-3 M, pH = 8.00, μ = 0.10 M
Solution 2:
[Citrate]total = 1.00 × 10-3 M, pH = 8.00, μ = 0.10 M
The calcium citrate solution gave an electrode reading of 25.90 mV.
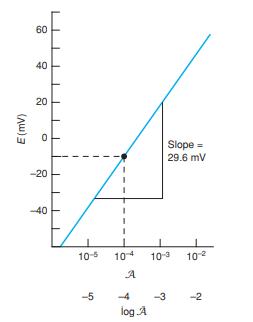
(a) Refer to the discussion with Figure B-2 in Appendix B. Calculate the activity of Ca2+ in the calcium citrate solution.
(b) Calculate the formation constant, Kf, for CaA-. Assume that the size of CaA- is 500 pm. At pH 8.00 and μ = 0.10 M, the fraction of free citrate in the form A3- is 0.998.
Figure B-2
Step by Step Answer:






