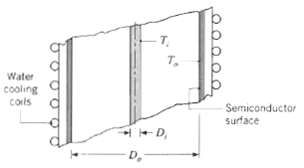
An arrangement for direct conversion of thermal energy to electrical power is shown. The inner cylinder of
Question:
An arrangement for direct conversion of thermal energy to electrical power is shown. The inner cylinder of diameter Di = 25 mm is heated internally by a combustion process that brings the ceramic cylinder (?i = 0.9) to a surface temperature of Ti = 1675?C. The outer cylinder of diameter Do = 0.38 m consists of a semiconductor material (? o = 0.5) that converts absorbed incident irradiation to electrical current; the backing material for the semiconductor is a highly conducting metal that is water cooled to 20?C. The converter is assumed to be very long compared to the outer diameter. The space between the two concentric cylinders is evacuated. Assuming diffuse, gray surfaces, determine the heat transfer rate per unit area of the outer cylinder. The electrical output of the semiconductor surface is 10% of the absorbed irradiation in the wavelength region 0.6 to 2.0?m. For the prescribed conditions, determine the power generation in watts per unit of outer surface area.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





