Boiler tubes exposed to the products of coal combustion in a power plant are subject to fouling
Question:
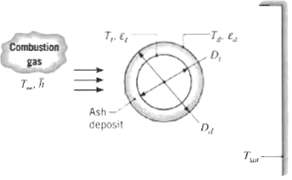
Boiler tubes exposed to the products of coal combustion in a power plant are subject to fouling by the ash (mineral) content of the combustion gas. The ash forms a solid deposit on the tube outer surface which reduces heat transfer to a pressurized water/steam mixture flowing through the tubes. Consider a thin- walled boiler tube (D t = 0.05 m) whose surface is maintained at T t = 600 K by the boiling process. Combustion gases flowing over the tube at T? = 1800 K provide a convection coefficient of h = 100 W/m2 ? K while radiation from the gas and boiler walls to the tube may be approximated as that originating from large surroundings at Tsut = 1500 K.
(a) If the tube surface is diffuse and gray, with ? t = 0.8, and there is no ash deposit layer, what is the rate of heat transfer per unit length, q', to the boiler tube?
(b) If a deposit layer of diameter D d = 0.06 m and thermal conductivity k = 1 W/m ? K forms on the tube, what is the deposit surface temperature, Td? The deposit is diffuse and gray, with ?d = 0.9, and Tt, T99, h, and Tsut remain unchanged. What is the net rate of heat transfer per unit length, q', to the boiler tube?
(c) Explore the effect of variations in Dd and h on q', as well as on relative contributions of convection and radiation to the net heat transfer rate. Represent your results graphically.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





