Question: Giant magneto resistance in a ferromagnetic metal, the conductivity ? p for electrons whose magnetic moments are oriented parallel to the magnetization is typically larger
Giant magneto resistance in a ferromagnetic metal, the conductivity ?p for electrons whose magnetic moments are oriented parallel to the magnetization is typically larger than ?a for those anti parallel to the magnetization. Consider a ferromagnetic conductor consisting of two separate regions of identical dimensions in series whose magnetizations can be independently controlled. Electrons of a given spin flow first through one region and then through the other. It is observed that the resistance when both magnetizations point upwards, R???is lower than the resistance when they point opposite, R??. This resistance change can be large for ?p/?a >> 1, and the phenomenon is called giant magneto resistance (GMR). A small external magnetic field can switch the resistance from R?? to R?? by reorienting the magnetization of the second layer. This effect is increasingly used in magnetic storage applications such as the magnetic bit readout in hard drives. The giant magneto resistance ratio is defined as:
(a) If there is no spin-flip scattering for the conduction electrons, show that
(b) If ?a ? 0, explain physically why the resistance in the ?? magnetization configuration is infinite.
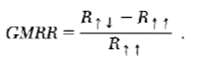
GMRR R-R1 R1
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Consider the resistance of the up and down spins separatel... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
14-P-S-S-G-P (89).docx
120 KBs Word File


