Question: In Figure a rectangular slab of slate rests on a bedrock surface inclined at angle = 26. The slab has length L = 43
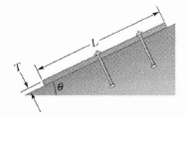
In Figure a rectangular slab of slate rests on a bedrock surface inclined at angle θ = 26. The slab has length L = 43 m, thickness Z = 2.5 m, and width 17 = 12 m, and 1.0 cm3 of it has a mass of 3.2 g. The coefficient of static friction between slab and bedrock is 0.39.
(a) Calculate the component of the gravitational force on the slab parallel to the bedrock surface.
(b) Calculate the magnitude of the static frictional force on the slab. By comparing (a) and (b), you can see that the slab is in danger of sliding. This is prevented only by chance protrusions of bedrock.
(c) To stabilize the slab, bolts are to be driven perpendicular to the bedrock surface (two bolts are shown). If each bolt has a cross-sectional area of.6.4 cm2 and will snap under a shearing stress of 3.6 x 108 N/m2, what is the minimum number of bolts needed? Assume that the bolts do not affect the normal force.
T
Step by Step Solution
3.28 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We denote the mass of the slab as m its density as p a... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
2-P-M-EE (245).docx
120 KBs Word File


