Question: A multilevel room and pillar metal mine is under consideration in flat strata striking N60E. Entries are planned on strike, crosscuts up, and down dip.
A multilevel room and pillar metal mine is under consideration in flat strata striking N60E. Entries are planned on strike, crosscuts up, and down dip. Table 6.8 shows depths and material properties associated with the geologic column. Rock properties data were determined from laboratory testing on NX-core at an L/D ratio of two. Stress measurements indicate that the premining stresses relative to compass coordinates are: Sv = 25d, Sh = 2,069 + 6.8d, SH = 3, 448 + 11.4d, where v = vertical, h = azimuth is 150?, H =azimuth is 60?, d =depth in m, and stress units are kPa. Three joint sets are present. Set 1 is vertical and strikes parallel to the strata. Set 2 strikes due north and dips 30? east; Set 3 also strikes due north, but dips 65? west. Joint properties for Mohr?Coulomb failure criteria are given in Table 6.9. Joint normal and shear stiffness (Kn, Ks) that relate normal stress and shear stress to corresponding displacements are also given in Table 6.9 as are the joint spacing?s (S). One mining plan calls for mining a lower B level 31.1 m in high and low grade ore at a depth of 290 and an upper A level of high grade ore 5.5 m thick at a depth of 281 m.
(a) Assume there is no size effect on compressive strength, then determine the maximum possible extraction ratio based on ore strength (ignore joints).
(b) Assuming square pillars, show in plan and vertical section, the relationship between rooms and pillars in the two levels that would be dictated by rock mechanics and explain your recommendation.
(c) What safety factor would you recommend for pillars in the upper and lower mining horizons and why?
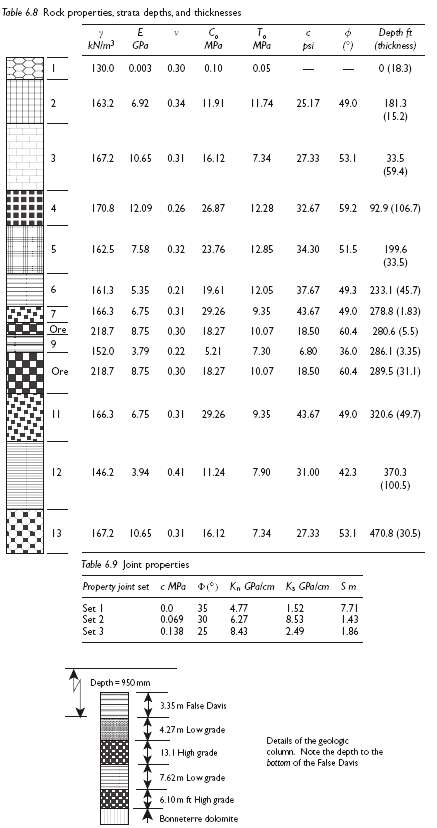
Table 6.8 Rock properties, strata depths, and thicknesses C. MPa T. MPa Depth ft (thickness) kNim GPa psi O (18.3) 130.0 0.003 0.30 0.10 0.05 163.2 6.92 0.34 11.91 I1.74 25.17 49.0 181.3 (15.2) 16.12 167.2 10.65 0.31 7.34 27.33 53.1 33.5 (59.4) 12.09 0.26 12.28 59.2 92.9 (106.7) 170.8 26.87 32.67 162.5 7.58 0.32 23.76 12.85 34.30 51.5 199.6 (33.5) 5.35 49.3 233.1 (45.7) 161.3 0.21 19.61 12.05 37.67 49.0 278.8 (1.83) 166.3 6.75 0.31 29.26 9.35 43.67 Ore 290.6 (5.5) 218.7 8.75 0.30 18.27 10.07 18.50 60.4 36.0 286.I (3.35) 152.0 3.79 0.22 5.21 7.30 6.80 218.7 18.27 60.4 289.5 (31.I) Ore 8.75 0.30 10.07 18.50 6.75 %3D 166.3 0.31 29.26 9.35 43.67 49.0 320.6 (49.7) 42.3 12 146.2 3.94 0.41 11.24 7.90 31.00 370.3 (100.5) 10.65 470.8 (30.5) 13 167.2 0.31 16.12 7.34 27.33 53.1 Table 6.9 Joint properties c MPa D) Kn GPalcm K, GPalam Property joint set Sm 0.0 Set I Set 2 Set 3 35 0.069 30 0.138 25 4.77 6.27 8.43 1.52 8.53 2.49 7.71 143 1.86 Depth = 950 mm 3.35m False Davis 4.27 m Low grade Details of the geologic column. Noce the depth to the bottom of the False Davis 13.I High grade 7.62m Low grade 6.10m ft High grade Bonneterre dolomite 3.
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Given Multilevel room and pillar metal mine table data geologic ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
26-E-G-R (272).docx
120 KBs Word File


