Question: Natural gas that contains methane, ethane, and propane is to be burned with humid air. The adiabatic flame temperature is to be calculated from specified
Natural gas that contains methane, ethane, and propane is to be burned with humid air. The adiabatic flame temperature is to be calculated from specified values of the following quantities: ycH4, yc2H6, yc3Hg = mole fractions of fuel components
Tf, Ta = inlet temperatures of fuel and air, ?C
Pxs = percent excess air
yw0 mole fraction of water in the inlet air
(b) For a basis of 1 g-mole of natural gas, calculate the gram-moles of each molecular species in the feed and product streams, assuming complete combustion and negligible CO formation. The answer should be expressed in terms of the variables given above.
(c) Given here are expressions for the specific enthalpies of the feed and product components relative to their elements at 25?C. Hi (kJ/mol) = ai ? biT + ciT2 + diT3 + eiT4, T in ?C. Derive the given expression for the specific enthalpy of methane from the heat capacity data in Table B.2. Then show that H for the reactor is given by an expression of the form ?H = a0 + a1T + a2T2 + a3T3 + a4T4?where T is the product temperature. Arid
(d) Write a spreadsheet program to take as input values of yCH4, YC3H8. Tf, Ta, Pxs, and yw0?and to solve the energy balance equation [?H (T) = 0] to determine the adiabatic flame temperature. Run the program for the following sets of input variable values: Suggestion: Near the top of the spreadsheet enter the values of a. b. c, d, and e for each species. Starting several rows below the last of these entries, list in Column A labels for the input variables and all calculated variables (component molar flow rates, specific enthalpies. Tad, a0, a1,. . . ,a4, ?f), and enter in adjacent columns the corresponding values or formulas for these variables in successive runs.?
(e) Write a computer program to carryout the above calculations using Newton?s rule (Appendix A.2), with an initial guess of 1000?C for each run. Build in a limit on the number of iterations in case the program fails to converge.
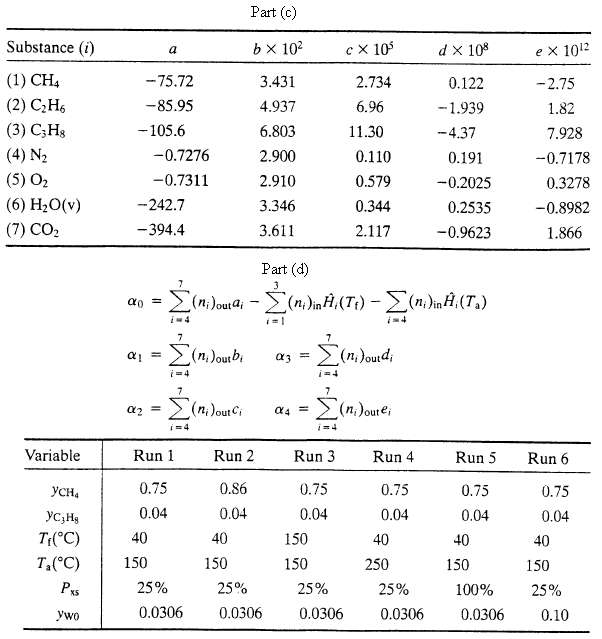
Substance (i) (1) CHA (2) C2H6 (3) C,Hg (4) N2 (5) 0 (6) H2O(v) (7) CO, Variable -75.72 -85.95 - 105.6 -242.7 -394.4 -0.7276 -0.7311 = YCHa YCjHg T(C) 40 Ta(C) 150 PxS ywo 0.75 0.04 (n. Jourbi i=4 Run 1 Part (d) = (ni)ouai - (n)ini (T) - (n)inf((.) i=4 25% 0.0306 Part (c) b102 3.431 4.937 6.803 2.900 2.910 3.346 3.611 Run 2 0.86 0.04 40 150 25% 0.0306 (=1 3 == ad 150 150 i=4 cx 10 Run 3 0.75 0.04 2.734 6.96 11.30 0.110 0.579 0.344 2.117 di 25% 0.0306 7=4 Dourei i=4 Run 4 0.75 0.04 40 250 d X 108 25% 0.0306 0.122 -1.939 -4.37 0.191 -0.2025 0.2535 -0.9623 Run 5 0.75 0.04 40 150 100% 0.0306 ex 1012 -2.75 1.82 7.928 -0.7178 0.3278 -0.8982 1.866 Run 6 0.75 0.04 40 150 25% 0.10
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
b 1 mol natural gas YCH mol CH4mol YCH mol CH6mol YCH mol CHgmol Humid air n mol air ywo mol H0vmol 1ywo mol dry airmol 021 mol Oymol DA 079 mol Nmol ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
13-E-C-E-C-P (573).docx
120 KBs Word File


