On January 1, 2011, Devco acquired cum div. all the shares of Brooke, at which date the
Question:
On January 1, 2011, Devco acquired cum div. all the shares of Brooke, at which date the equity and liability sections of Brooke’s statement of financial position showed the following balances:
Share capital (300,000 shares)………………….. $300,000
Retained earnings ……………………………… 40,000
Other components of equity……………………. 30,000
Dividend payable……………………………….. 20,000
The dividend payable was subsequently paid in February 2011.
On January 1, 2011, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Brooke were recorded at fair value except for:

The inventory was all sold by October 2011. The machinery had a further five-year life but was sold on June 30, 2013. At the acquisition date, Brooke had a contingent liability of $20,000 that Devco considered to have a fair value of $12,000. This liability was settled in December 2011. At January 1, 2011, Brooke had not recorded any goodwill. On December 31, 2013, the trial balances of Devco and Brooke were as follows:
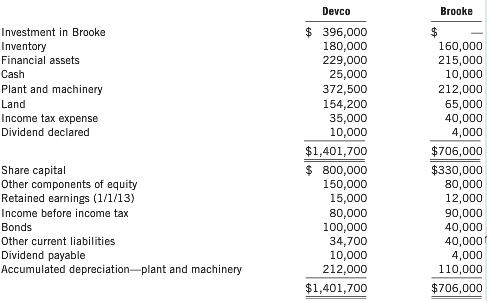
Additional information:
1. On January 1, 2012, Devco sold an item of plant to Brooke at a profit before tax of $4,000. Devco depreciates this particular item of plant straight line over 5 years and Brooke depreciates straight line over 10 years.
2. At December 31, 2013, Devco had on hand some items of inventory purchased from Brooke in June 2013 at a profit of $500.
3. Devco charged a management fee of $2,000 per month to Brooke. As of year end, Brooke had not paid the fee for three months.
4. The tax rate is 30%.
Required
(a) Prepare the consolidated statement of comprehensive income, consolidated statement of changes in equity, and the consolidated statement of financial position at December 31, 2013.
(b) In relation to part (1) in the additional information, explain why you made the consolidated financial statement adjustments at December 31, 2013.
Carrying amount $120,000 160,000 Fair value Inventory Machinery (cost $200,000) $130,000 165,000 Devco Brooke Investment in Brooke Inventory Financial assets Cash Plant and machinery Land Income tax expense Dividend declared $396,000 180,000 229,000 25,000 372,500 154,200 35,000 10,000 160,000 215,000 10,000 212,000 65,000 40,000 4,000 $706,000 $330,000 80,000 12,000 90,000 40,000 40,000 4,000 110,000 $706,000 $1,401,700 Share capital Other components of equity Retained earnings (1/1/13) Income before income tax Bonds Other current liabilities Dividend payable Accumulated depreciation-plant and machinery $800,000 150,000 15,000 80,000 100,000 34,700 10,000 212,000 $1,401,700 JUPITER INC. &EUROPA LTD. Statements of Income and Retained Earning:s year ended December 31, 2013 upiter Europa Sales Investment income $12,280,000 240,000 $7,370,000 12,000 7,382,000 12,520,000 Cost and expenses Cost of goods sold Depreciation and amortization expense Interest expense Other expenses Income tax expense 7,859,000 531,000 212,000 793,000 1,250,000 10,645,000 1,875,000 1,722,000 3,597,000 625,000 $ 2,972,000 5,159,000 350,000 152,000 356,000 546,000 6,563,000 819,000 1,300,000 2,119,000 240,000 $1,879,000 Net income Retained earnings, beginning of year Dividends Retained earnings, end of year JUPITER INC. &EUROPA LTD. Balance Sheets December 31, 2013 Jupiter Europa Assets Cash and receivables Inventory Investment in Europa Loan to Jupiter (non-current) Property, plant and equipment (net) 串1,516,000 4,124,000 4,716,000 $976,000 2,850,000 4,716,000 $15,116,000 300,000 5,756,000 $9,882,000 Liabilities and shareholders' equity Current liabilities Long-term liabilities Common shares Retained earnings $2,844,000 5,300,000 4,000,000 2,972,000 $15,116,000 $1,203,000 3,800,000 3,000,000 1,879,000 $9,882,000 HIT PUC Sales and other income Less expenses Cost of goods sold Depreciation expense Income tax and other expenses Net income $28,800,000 $13,000,000 18,000,000 3,400,000 4,200,000 3,200,000 8,200,000 1,800,000 1,600,000 1,400,000 HIT $15,000,000 28,600,000 $43,600,000 PUC $ 8,800,000 17,400,000 $26,200,000 $13,800,000 Current assets Non-curent assets Total assets Liabilities Common Shares Retained Earnings Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $26,400,000 4,000,000 13,200,000 $43,600,000 2,000,000 10,400,000 $26,200,000 Sienna Danon $234,800 17,000 6,600 $190,000 Sales revenue Dividend revenue Other income 10,000 200,000 (120,000) (20,000) (140,000) 60,000 (20,000) 40,000 32,000 72,000 (9,800) (7,200) (17,000) $55,000 258,400 (123,000) (34,600) (157,600) 100,800 (32,000) Cost of sales Other expenses Profit before income tax Net income Profit for the year Retained earnings (1/1/13) Total available for appropriation Interim dividend paid Dividend declared 68,800 76,000 144,800 (34,000) (16,000) (50,000) 94,800 Retained earnings (31/12/13) Current assets Cash Receivables Allowance for doubtful accounts Financial assets Inventory Total current assets Non-current assets Plant and machinery Accumulated depreciation Land Bonds in Danon Investment in Danon Total non-current assets $1,000 27,000 (500) 20,000 48,000 95,500 40 12,100 (300) 10,000 47,000 68,840 70,000 (26,000) 190,000 100,000 (40,000) 99,300 60,000 160,000 379,300 474,800 234,000 302,840 Total assets Sienna Danon Current liabilities Dividend payable Provisions Bank overdraft Current tax liabilities 7,200 8,800 14,840 10,000 40,840 16,000 12,000 11,000 39,000 Total current liabilities Non-current liabilities 5% mortgage bonds Deferred tax liabilities 13,000 13,000 52,000 $422,800 80,000 5,000 85,000 125,840 $177,000 Total non-current liabilities Total iabilities Net assets Equity Share capital Retained earnings Other components of equity Total equity $320,000 94,800 8,000 $422,800 $120,000 55,000 2,000 $177,000 Coltron Tara $25,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 28,000 21,000 3,000 24,000 4,000 1,350 2,650 6,000 8,650 2,500 $23,600 Sales revenue Dividend revenue Other income Gain on sale of property, plant, and equipment Tota Cost of sales Other expenses Total expenses Profit before income tax Income tax expense Profit for the period Retained earnings (1/1/13) 2,000 2,000 27,600 18,000 1,000 19,000 8,600 1,950 6,650 3,000 9,650 1,000 $ 8,650 Dividend paid Retained earnings (31/12/13) 6,150 Jasmine Lessard $40,000 3,000 1,600 44,600 30,000 7,500 37,500 7,100 2,200 4,900 2,800 7,700 2,000 2,400 4,400 $3,300 $78,000 Revenue Gain on sale of office furniture Dividend revenue Total income Cost of sales Other expenses Total expenses Profit before income tax Income tax expense Profit for the year Retained earnings (1/1/13) 4,400 82,400 60,000 10,800 70,800 11,600 3,000 8,600 14,500 23,100 4,000 8,000 12,000 $11,100 Interim dividend paid Final dividend declared Retained earnings (31/12/13) Jasmine Lessard Retained earnings Share capital 39,500 50,000 6,800 40,000 Plant and equipment (cost $80,000) nventory Carrying amount F value $61,000 3,500 $60,000 3,000 Carrying amount Fair value Inventory Plant (cost $80,000) $10,000 50,000 $12,000 53,000 Abbots Evion $146,000 9,000 2,000 157,000 88,000 16,000 104,000 53,000 12,000 41,000 10,000 51,000 8,000 $43,000 $120,000 Sales Dividend revenue Gain on sale of non-current asset 120,000 68.000 19,000 87,000 33,000 14,000 19,000 10,000 29,000 9,000 $ 20,000 Cost of sales Other expenses Profit before income tax Income tax expense Profit for the year Retained earnings (1/4/13) Total available for appropriation Dividend paid Retained earnings (31/3/14) Trial Balances as at December 31, 2013 Lara ade Credits Share capital Retained earnings (1/1/13) Current tax liabilities Deferred tax liabilities Payables Sales revenue Other income $500,000 90,000 22,000 6,240 22,000 250,000 20,000 $910,240 $100,000 86,000 38,000 5,200 14,000 120,000 5,000 $368,200 Debits Income tax expense Dividend declared and paid Property, Plant, and Equipment -net Motor vehicles-net Receivables Financial assets Inventory Cash Deferred tax assets Investment in Jade Cost of sales Other expenses Loss on sale of property, plant, and equipment sold 20,000 10,000 125,000 124,200 25,000 60,000 106,440 46,900 12,700 160,000 188,000 28,000 4,000 $10,000 8.000 76,000 52,600 7,310 40,000 72,000 5,990 6,300 80,000 5,000 5,000 $368,200 910,240 Carrying amount Inventory Motor vehicles (cost $18,000) Furniture and fixtures (cost $30,000) Land $50,000 15,000 24,000 18,480 Fair value $56,000 16,000 32,000 24,480 Tilford Sifton Credits Share capital Retained earnings (1/1/13) Bonds Final dividend payable Current tax liabilities Other payables Advance from Tilford Sales revenue Other income Accumulated depreciation $170,000 57,000 120,000 10,000 8,000 34,800 $80,000 51,500 3,000 2,500 10,100 10,000 65,000 22,000 85,000 23,000 - Motor vehicles - Furniture and fixtures 4,000 2,000 $513,800 2,000 6,000 $252,100 Debits Cost of sales Other expenses Investment in Sifton Land Motor vehicles Furniture and fixtures Inventory Other assets Income tax expense Interim dividend paid Final dividend declared Deferred tax assets Advance to Sifton $65,000 22,000 137,200 53,500 27,000 28,000 34,000 171,580 8,620 7,200 4,000 10,000 16,200 10,000 $513,800 24,480 22,000 37,300 70,320 3,100 2,000 2,000 3,000 7,400 $252,100 Miran Winter $234,800 17,000 6,600 $190,000 Sales revenue Dividend revenue Other income 258,400 (123,000) (34,600) (157,600) 100,800 (32,000) 68,800 76,000 144,800 10,000 200,000 (120,000) (20,000) (140,000) 60,000 (20,000) 40,000 32,000 72,000 (9,800) (7,200) (17,000) $55,000 Cost of sales Other expenses Profit before income tax Income taxes Profit for the year Retained earnings (1/1/13) Total available for appropriation Interim dividend paid Dividend declared (34,000) (16,000) (50,000) 94,800 Retained earnings (31/12113) Current assets Cash Receivables Allowance for doubtful accounts Financial assets Inventory Total current assets $1,000 27,000 (500) 20,000 48,000 95,500 40 12,100 (300) 10,000 47,000 68,840 Non-current assets Plant and machinery Accumulated depreciation Land Bonds in Winter Investment in Winter 70,000 (26,000) 190,000 100,000 (40,000) 99,300 60,000 160,000 379,300 Total non-current assets 234,000 302,840 Total assets 474,800 Current liabilities Dividend payable Provisions Bank overdraft Current tax liabilities Total current liabilities Non-current liabilities 5% mortgage bonds Deferred tax liabilities Total non-current liabilities Total liabilities Net assets 16,000 12,000 11,000 39,000 7,200 8,800 14,840 10,000 40,840 13,000 13,000 52,000 $422,800 80,000 5,000 85,000 125,840 $177,000 Equity Share capital Retained earnings Other components of equity Total equit) $320,000 94,800 8,000 $422,800 $120,000 55,000 2,000 $177,000
Step by Step Answer:
Consideration transferred 396000 Net fair value of identifiable assets and liabilities of Brooke 350000 300000 Share capital 40000 Retained earnings 30000 Other equity 20000 Dividend payable Fair valu...View the full answer



Students also viewed these Accounting questions
-
The City Commission of Nashville has decided to build a botanical garden and picnic area in the heart of the city for the recreation of its citizens. The precedence table for all the activities...
-
1. On January 1, 2016 Du Lac Company purchased office equipment that cost $16,000 cash. The equipment had a five year useful life and a $1,200 expected salvage value. Using straight line...
-
On January 1, 2011, Greg's Grocery purchased a truck for $41,000 that has an estimated useful life of five years and a $1,000 residual value. Greg uses the straight-line depreciation method. Record...
-
The time it takes to get a cars oil changed at Speedy Lube is distributed normally with a mean of 12 min and a standard deviation of 2 min. Compute the probability that a customer will have her or...
-
Does Sec. 351 require shareholders to receive stock equal in value to the property transferred? Suppose Fred and Susan each transfer property worth $50,000 to Spade Corporation. In exchange, Fred...
-
On October 31, 2021, Cullumber Company had a cash balance per books of $8,967. The bank statement on that date showed a balance of $10,163. A comparison of the statement with the Cash account...
-
Between what values do the IQ scores of 95% of all rural Midwest seventhgraders lie?
-
1. How does the information technology development for video-based businesses differ from traditional businesses? 2. What challenges do these types of companies face in relation to the rapid changes...
-
There is only one floor plan at Apple Apartments. The first floor rents for $ 9 0 0 , the second floor rents for $ 8 0 0 and the third floor rents for $ 9 7 5 . If you sign a 1 3 - month lease you...
-
Bradburn Corporation was formed 5 years ago through a public subscription of common stock. Daniel Brown, who owns 15% of the common stock, was one of the organizers of Bradburn and is its current...
-
Alexis owns 100% of the shares of Ruby. During 2013, the following events occurred: 1. Alexis sold inventory for $10,000 that had been sold to it by Ruby in December 2012. The inventory originally...
-
P4-2 Summer Corp. owns all the shares of Keira Ltd. The shares were acquired on July 1, 2011, by Summer at a cost of $60,000. At acquisition date, the capital of Keira consisted of 44,000 common...
-
On January 2, 2019, Magee, Inc., purchased, as a stock investment, 20,000 shares of Dye, lnc.'s common stock for $21 per share, including commissions and taxes. On December 31, 2019, Dye announced a...
-
Write out the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the function (see example). Do not determine the numerical values of the coefficients. x3 (a) x + 7x+6 9x+1 (b) (x + 1)3(x + 2) Submit...
-
You desire to make an 80% by weight vinyl acetate to 20% by weight styrene copolymer via free radical, emulsion polymerization. The r 1 and r 2 values for these monomers are 0.01 and 55,...
-
Q1)In a wheel and axle machine the diameters of the wheel and the axle are 450mm and 60mm respectively.The efficiency is 97%(0.97 per unit).When a body having a mass of 40kg is being lifted.Determine...
-
Smith & Chief Ltd. of Sydney, Australia, is a merchandising firm that is the sole distributor of a product that is increasing in popularity among Australian consumers. The company's income statements...
-
C. In lab, you measure the x & y components of a possible incompressible flow field as u = 2cxy; and where cand a are constants. v = c(a + x - y) 5. (04 pts) Short answer, what is necessary for the...
-
Resolve Problem 19 including damping. Discuss the importance of damping by comparing the two results. Problem 19: Structures are sometimes subjected to very rapidly applied loads of extremely short...
-
The percentage of completion and completed contract methods are described in the FASB ASC. Search the codification to find the paragraphs covering these topics, cite them, and copy the results.
-
The energy dissipated over the following duration is considered in finding the equivalent viscous-damping constant of a system with Coulomb damping: a. half cycle b. full cycle c. one second
-
What is the accounting concept of a business combination?
-
Is dissolution of all but one of the separate legal entities necessary in order to have a business combination? Explain.
-
Is dissolution of all but one of the separate legal entities necessary in order to have a business combination? Explain.
-
Problem Set Time Value of Money 1. In 10 years, what is the value of $100 invested today at an interest rate of 8% per year, compounded annually? 2. In 10 years, what is the value of $100 invested...
-
The Blending Department of Luongo Company has the following cost and production data for the month of April. Costs: Work in process, April 1 Direct materials: 100% complete $120,000 Conversion costs:...
-
Q3 plz answer correctly and check work Builtrite's upper management has been comparing their books to industry standards and came up with the following question: Why is our operating profit margin...

Study smarter with the SolutionInn App


