A plate (k = 10W/m K) is stiffened by a series of longitudinal ribs having a
Question:
A plate (k = 10W/m ∙ K) is stiffened by a series of longitudinal ribs having a rectangular cross section with length L = 8 mm and width w = 4 mm. The base of the plate is maintained at a uniform temperature Tb = 45°C, while the rib surfaces are exposed to air at a temperature of Tx = 25°C and a convection coefficient of h = 600W/m2 ∙ K.
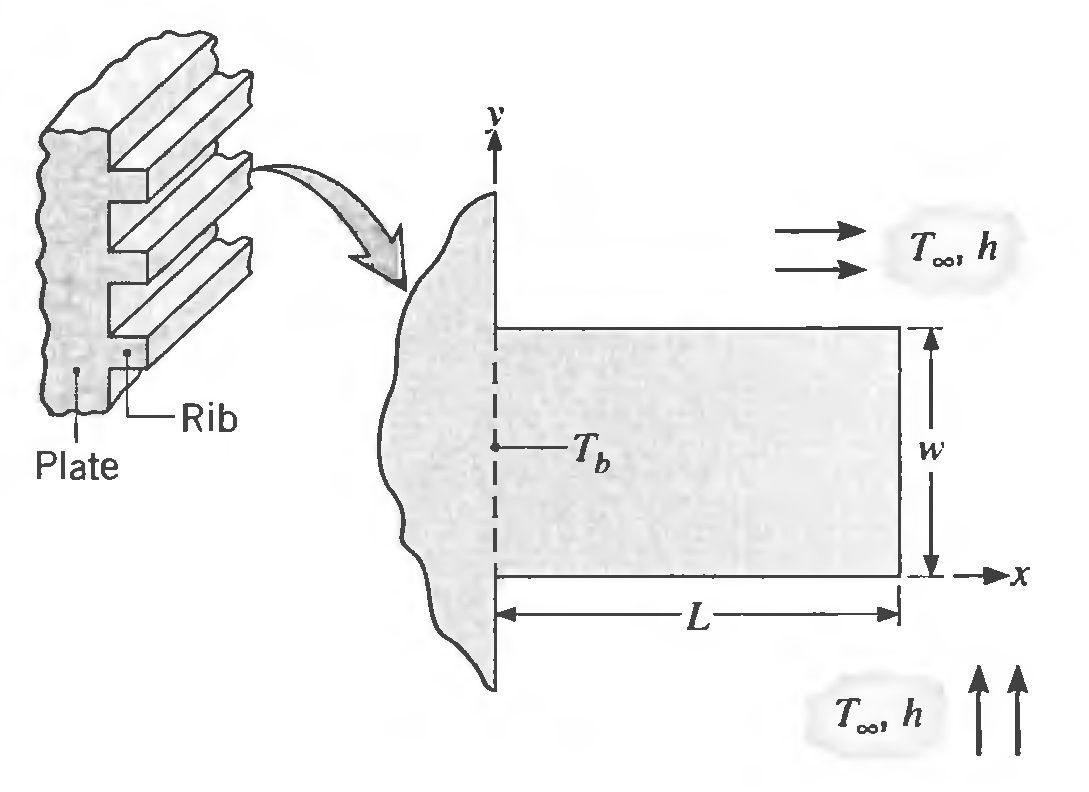
(a) Using a finite-difference method with ∆x = ∆y = 2 mm and a total of 5 x 3 nodal points and regions, estimate the temperature distribution and the heat rate from the base. Compare these results with those obtained by assuming that heat transfer in the rib is one-dimensional, thereby approximating the behavior of a fin.
(b) The grid spacing used in the foregoing finite difference solution is coarse, resulting in poor precision for estimates of temperatures and the heat rate. Investigate the effect of grid refinement by reducing the nodal spacing to ∆x = ∆y = 1 mm (a 9 x 3 grid) considering symmetry of the center line.
(c) Investigate the nature of two-dimensional conduction in the rib and determine a criterion for which the one-dimensional approximation is reasonable. Do so by extending your finite-difference analysis to determine the heat rate from the base as a function of the length of the rib for the range 1.5 < L/w < 10, keeping the length L constant. Compare your results with those determined by approximating the rib as a fin.
DistributionThe word "distribution" has several meanings in the financial world, most of them pertaining to the payment of assets from a fund, account, or individual security to an investor or beneficiary. Retirement account distributions are among the most...
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





