A compression-ignition engine runs on a fuel of the following analysis by weight: carbon (84 %), hydrogen
Question:
A compression-ignition engine runs on a fuel of the following analysis by weight: carbon \(84 \%\), hydrogen \(16 \%\). If the pressure at the end of combustion is 55 bar, the volume ratio of expansion is \(15: 1\), the pressure and temperature at the end of expansion are \(1.75 \mathrm{bar}\) and \(600^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) respectively, calculate:
a. the variable specific heat at constant volume for the products of combustion; and
b. the change in entropy during the expansion stroke per kg molecule.
The expansion follows the law \(p V^{n}=\mathrm{C}\) and there is \(60 \%\) excess air. The specific heats at constant volume in \(\mathrm{kJ} / \mathrm{kmol} \mathrm{K}\) between \(600{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(2400{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) are:
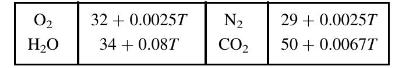
The water vapour \(\left(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right)\) may be considered to act as a perfect gas. [(a) \(22.1+0.0184 T\); (b) \(-11.42 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{kmol} \mathrm{K]}\)
Step by Step Answer:

Advanced Thermodynamics For Engineers
ISBN: 9780080999838
2nd Edition
Authors: D. E. Winterbone, Ali Turan





