Question:
Calculate the small-signal voltage gain of a common-source amplifier with depletion load in Fig. 4.20, including both the body effect and channel-length modulation. Assume that V
DD= 3 V and that the dc input voltage is adjusted so that the dc output voltage is 1 V. Assume that M
1has drawn dimensions of W = 100 µm and L = 1 µm. Also, assume that M
2has drawn dimensions of W = 10 µm and L = 1 µm. For M
2, assume V
t0= ˆ’1 V. For both transistors, assume that X
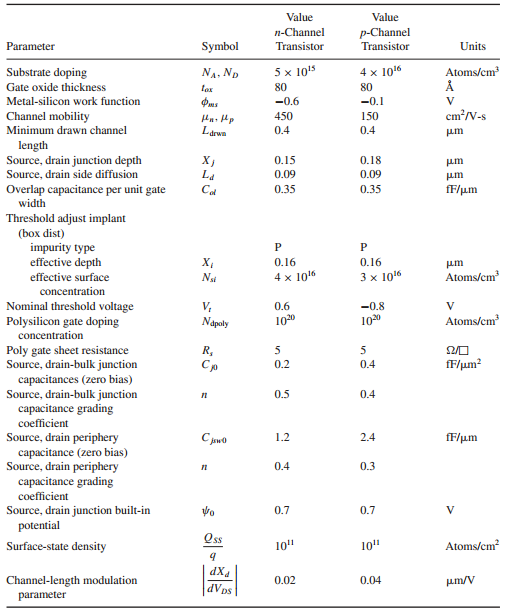
d= 0. Use Table 2.4 for other parameters of both transistors.
Figure 4.20:
(a) Common-source amplifier with depletion-mode transistor load. (b) dc transfer characteristic.
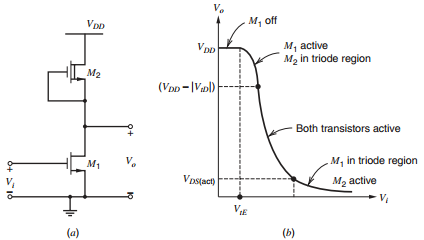
Table 2.4:
Transcribed Image Text:
V. M, off VpD M, active M, in triode region V pD M2 (VDD -|Val) Both transistors active M, in triode region V. M1 M2 active Vpsjact) VE (b) (a) Value Value n-Channel p-Channel Parameter Symbol Transistor Transistor Units Substrate doping Gate oxide thickness 5 x 105 Atoms/cm NA, Np 4 x 106 Гоx 80 80 Metal-silicon work function Фия -0.6 -0.1 cm?/V-s Channel mobility Minimum drawn channel 450 150 Larwn 0.4 0.4 μη length Source, drain junction depth Source, drain side diffusion Overlap capacitance per unit gate X) La 0.15 0.18 um 0.09 0.09 0.35 0.35 fF/um width Threshold adjust implant (box dist) impurity type effective depth effective surface х, 0.16 0.16 Nsi 4 x 1016 3 x 1016 Atoms/cm concentration Nominal threshold voltage Polysilicon gate doping concentration V, Napoly 0.6 100 -0.8 1020 Atoms/cm R, ΩΟ Poly gate sheet resistance Source, drain-bulk junction fF/um? Cp 0.2 0.4 capacitances (zero bias) Source, drain-bulk junction capacitance grading 0.5 0.4 coefficient Source, drain periphery capacitance (zero bias) Source, drain periphery Срно 1.2 2.4 fF/um 0.4 0.3 capacitance grading coefficient Source, drain junction built-in potential 0.7 0.7 Os Surface-state density 10" 10" Atoms/cm? Channel-length modulation parameter PXP dVps 0.02 0.04 um/V









