Consider Example 16.7. Make following modifications. For each modification, solve the optimization problems when the objective function
Question:
Consider Example 16.7. Make following modifications. For each modification, solve the optimization problems when the objective function is the operating cost and when the objective function is the before-tax NPV.
In Example 16.7, the methanol synthesis reactor has been assumed to be isothermal and its temperature is considered to be a decision variable. Since the overall methanol synthesis reaction is highly exothermic, large amount of heat must be removed. This can be done by generating steam. Considering medium pressure steam is being produced, assume the thermal fluid is at a constant temperature of 184°C. Keeping the same dimensions for the tubes as in Example 16.7, consider the number of tubes in the reactor as a decision variable as opposed to the reactor temperature in Example 16.7. Modify the operating cost calculation by including the revenue earned due to generation of the medium pressure steam. For calculating the capital cost of the reactor, consider the cost and volume calculated in Example 16.7 as the base cost and volume of the reactor and then calculate the updated cost using the updated volume using six-tenths rule. For calculating the volume of the reactor, assume the total volume of the reactor is a fixed multiple of the volume occupied by the tubes.
Under optimal condition, about 2% product is being lost in the methanol purification column overhead. In Example 16.7, the condenser temperature is constrained to be higher than 35°C. One way to reduce the methanol loss further will be to reduce the condenser temperature by using a refrigerant. Consider possible use of a refrigerant and then consider the condenser temperature as an additional decision variable. Modify the equations for optimization objectives by including the cost of refrigeration.
Example 16.7
Consider the flowsheet in Figure E16.7.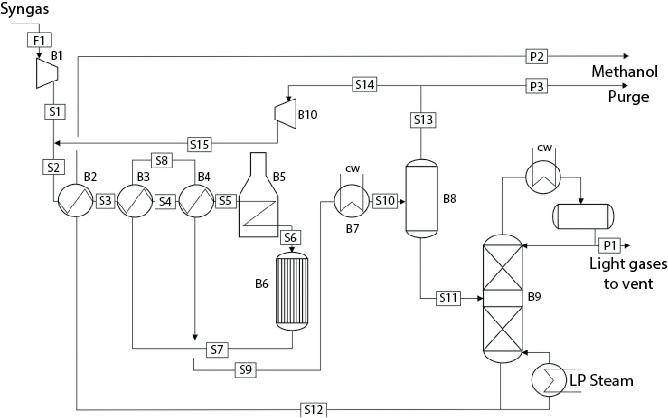
Stream F1 has the following properties: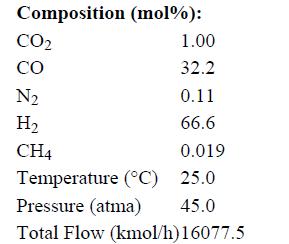

![CO2 + 3H2 CH3OH + HO CO2+H2 = CO+H2O The rate equations are obtained from Van-Dal and Boullaou [15]:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/3/5/5/142654a1a06b5d021699355138910.jpg)
![T1 72 Den = 1.07x103 kmol kgcats ( 1.22x107 exp kmol kgcats kJ mol RT[K] -10 exp Den -98.084 (1) (0, mol](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/3/5/5/167654a1a1fbca711699355163801.jpg)
Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





