Consider the reactor in Example 22.9 using an inlet oxylene partial pressure of 0.0175 bar. Without dilution,
Question:
Consider the reactor in Example 22.9 using an inlet oxylene partial pressure of 0.0175 bar. Without dilution, this feed concentration leads to a runaway condition in the reactor. Explore the possibility of diluting the catalyst.
Example 22.9
The synthesis of phthalic anhydride from o-xylene is considered. The following parameters and pseudo-firstorder reaction rate may be used for an approximate preliminary design of a shell-and-tube reactor.![]()
The autoignition temperature of o-xylene = 465°C and lower explosion limit (LEL) = 0.9% at room temperature.
Data: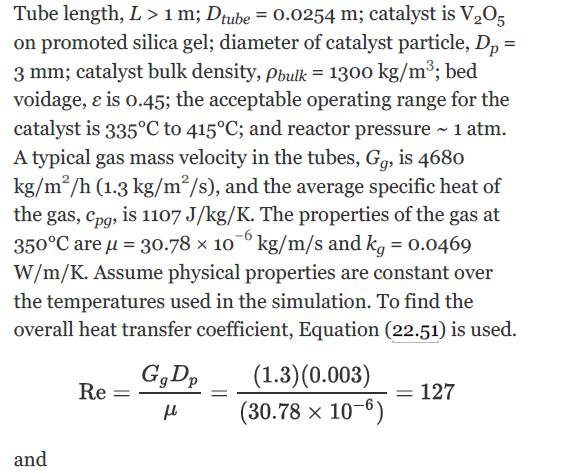
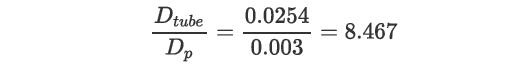
which are in the correct range to use Equation (22.51),![hw,eff Dtube kg (2.03) (127) 0.8 exp[-8.467] = 48.17 (48.17) (0.0469) = 88.9 W/m/K (0.0254) andUhw,eff = 88.9](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1699/4/3/9/614654b63fe304681699439613312.jpg)
The reaction rate can be approximated by a pseudo-firstorder equation: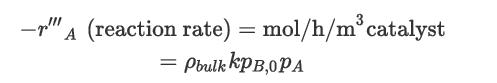
where Component A is o-xylene, k = 4.122 × 108e−13,636/T[K] mol/h/bar2/kg (catalyst), and Component B is oxygen with an initial partial pressure, pB,o = 0.21 bar.
The average heat of reaction for this temperature range −ΔHr is 1150 kJ/mol.
For illustration purposes, it is assumed that cooling takes place by heat exchange with a cooling medium flowing through the shell side at 335°C that vaporizes at constant pressure and temperature. With this assumption, the shell-side temperature, Tcool, is fixed at 335°C.
Determine the temperature profiles in the tube for partial pressures of o-xylene in the feed ranging from 0.01 to 0.02. Assume that the effect of changing pressure is small; that is, assume constant pressure conditions and a process gas inlet temperature of 335°C.
Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





