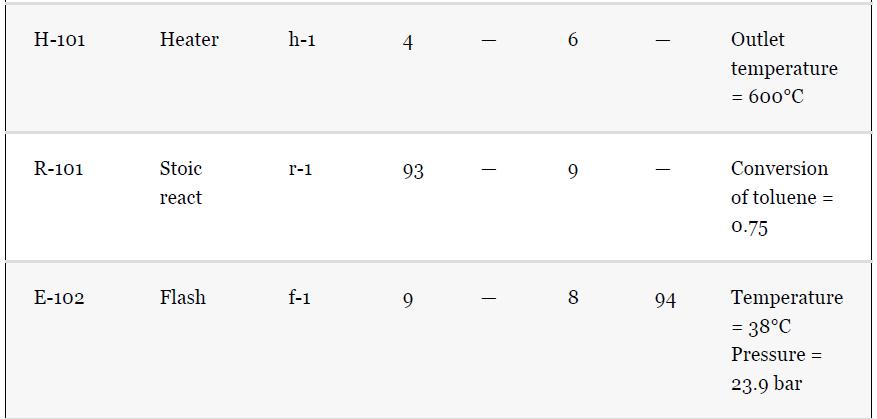
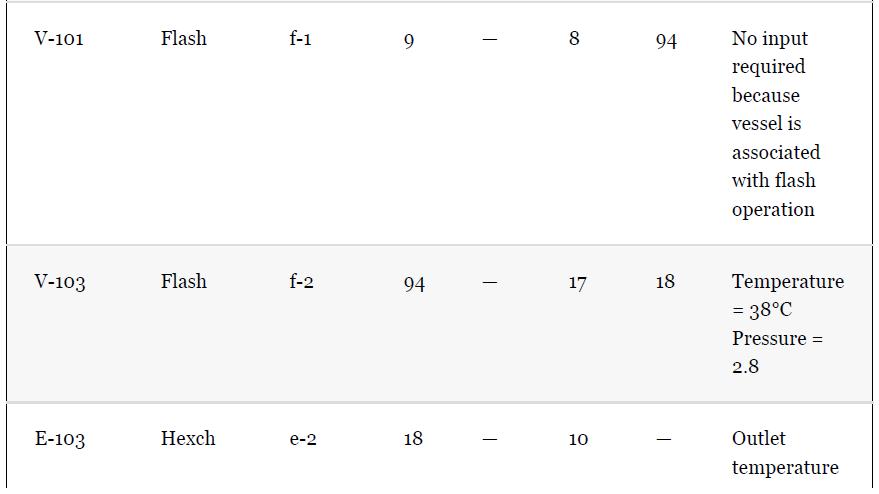
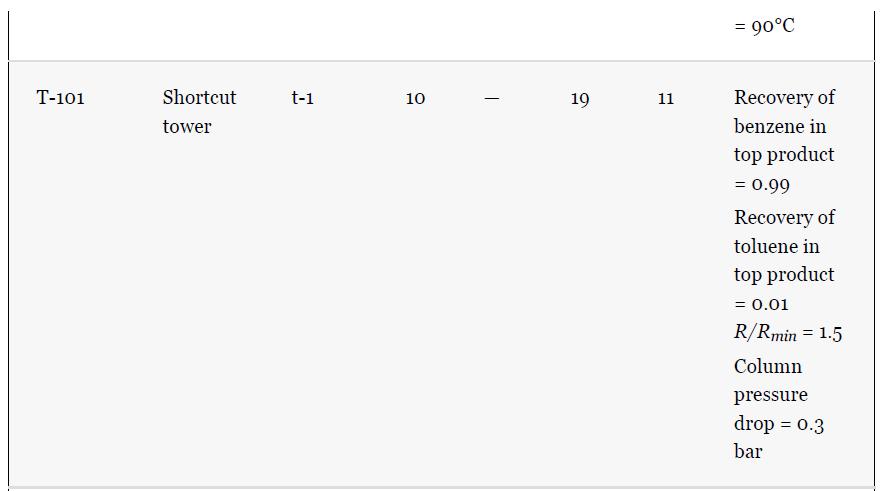
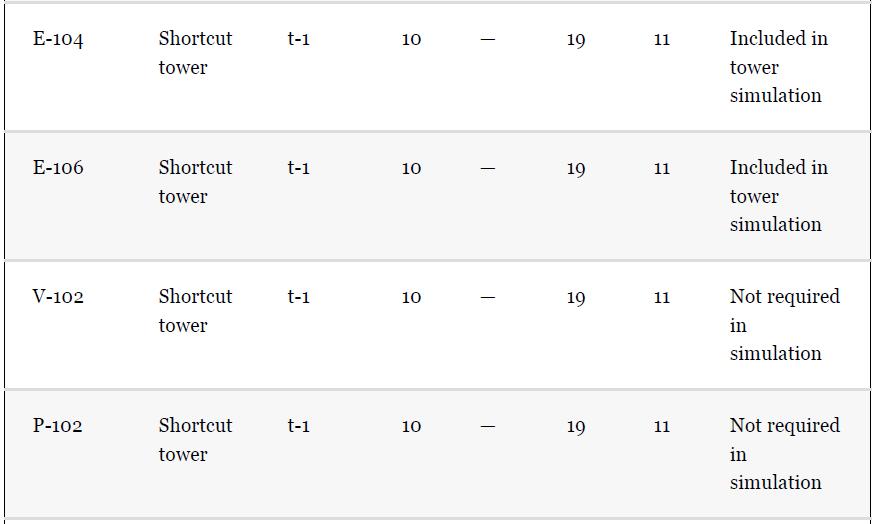
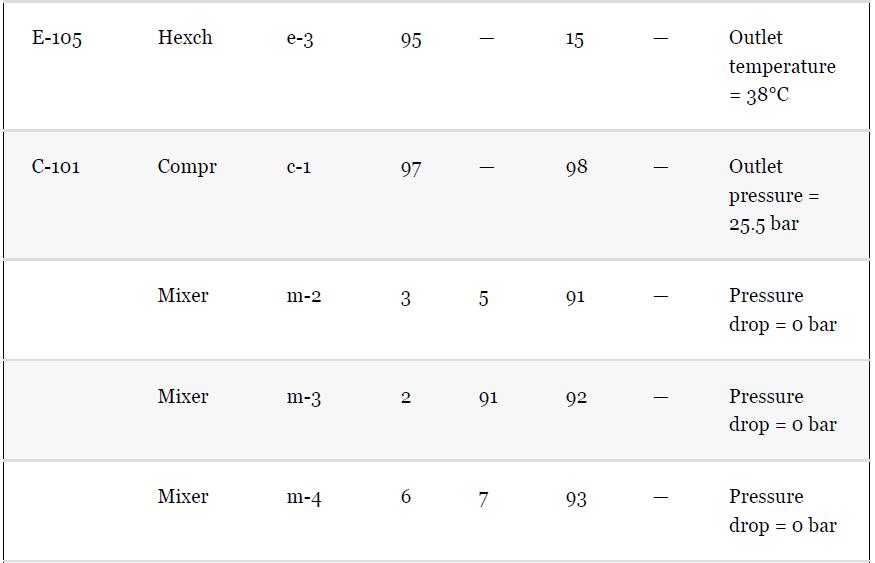
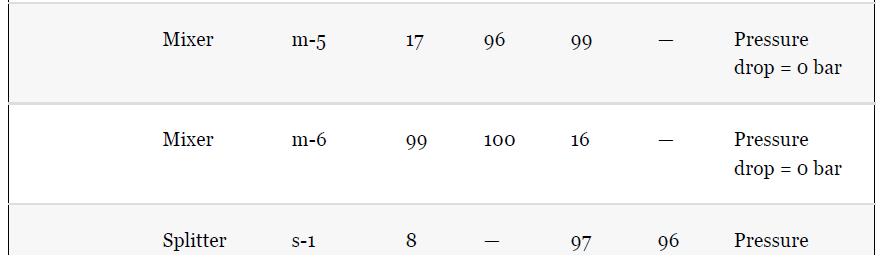
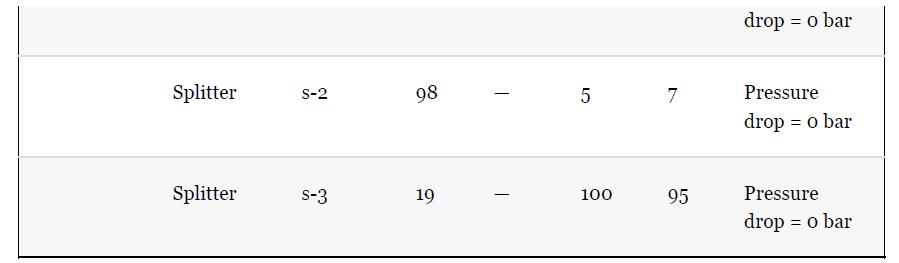
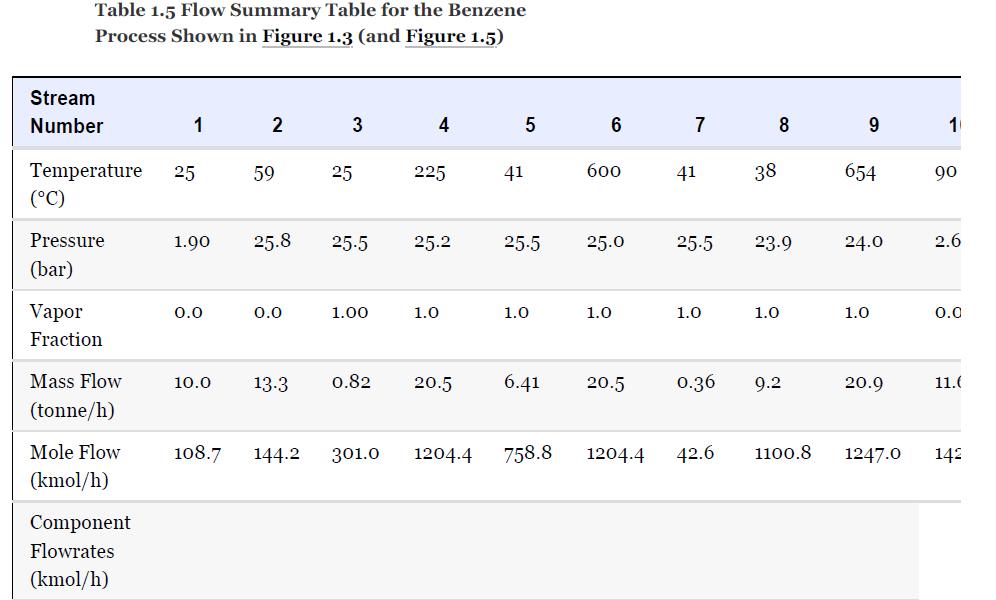
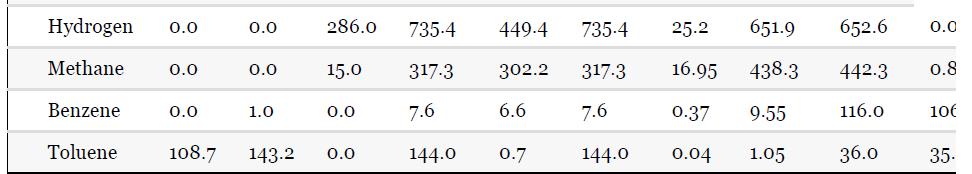
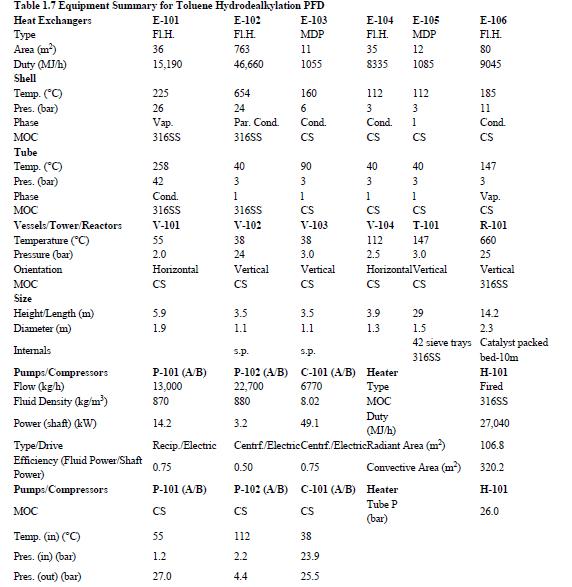
Using the results from Problem 13.7 and Tables 1.5 and 1.7, compare the results for the simulation
Question:
Using the results from Problem 13.7 and Tables 1.5 and 1.7, compare the results for the simulation of the benzene recovery column, T-101, using a shortcut method and a rigorous method. One way to do this comparison is to use the number of theoretical plates from the shortcut method as an input to the rigorous method. The rigorous method is used to simulate the same separation as the shortcut method, that is, the same overhead purity and recovery. The difference in the methods is then reflected by the difference between the reflux required for both methods. Comment on the difference for this nearly ideal system. Remember that there is no need to simulate the whole flowsheet for this problem; just use the input to the column from Table 1.5.
Problem 13.7
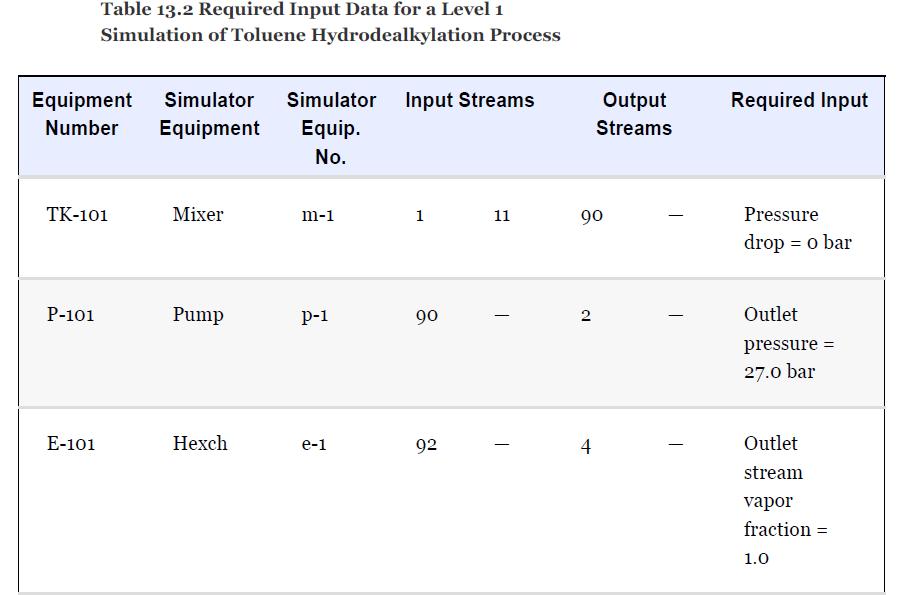
For the toluene HDA process, using the data given in Tables 13.1 and 13.2, simulate the process and compare the results with those given in Chapter 1, Table 1.5. Remember that the number of actual plates is given in Table 1.7, and an efficiency of 0.6 was assumed.




Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





