A dimensionless grouping of variables and parameters that are important in pipe flow is called the Reynolds
Question:
A dimensionless grouping of variables and parameters that are important in pipe flow is called the Reynolds number:
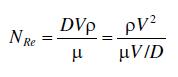
where
$V$ is the average velocity over the cross section in a pipe of diameter $D$
$ho$ is the fluid density
$\mu$ is the fluid viscosity
Comparing the numerator and denominator of the RHS of the equation with Equations 1.16 and 1.11 shows that this group is a ratio of the convective (turbulent) momentum flux to the laminar (viscous) momentum flux, or the ratio of (destabilizing) inertia forces to (stabilizing) viscous forces. Thus, at low values of the Reynolds number, viscous forces dominate and the flow is smooth and stable (laminar), and at high Reynolds numbers, inertial forces dominate and the flow is unstable (turbulent). It has been found that laminar flow occurs in a pipe only when the Reynolds number is less than about 2000. Calculate the maximum velocity and the corresponding volumetric flow rate (in $\mathrm{cm}^{3} / \mathrm{s}$ ) at which laminar flow of air and water is possible in pipes with the following diameters:
![]()
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781498724432
3rd Edition
Authors: Ron Darby, Raj P Chhabra





