A manometer with mercury as the manometer fluid is attached to the wall of a closed tank
Question:
A manometer with mercury as the manometer fluid is attached to the wall of a closed tank containing water (see Figure P4.30). The entire system is rotating about the axis of the tank at $N$ rpm. The radius of the tank is $r_{1}$, the distances from the tank centerline to the manometer legs are $r_{2}$ and $r_{3}$ (as shown), and the manometer reading is $h$. If $N=30 \mathrm{rpm}, r_{1}=12 \mathrm{~cm}, r_{2}=15 \mathrm{~cm}$, $r_{3}=18 \mathrm{~cm}$, and $h=2 \mathrm{~cm}$, determine the gage pressure at the wall of the tank and also at the centerline at the level of the pressure tap on the tank.
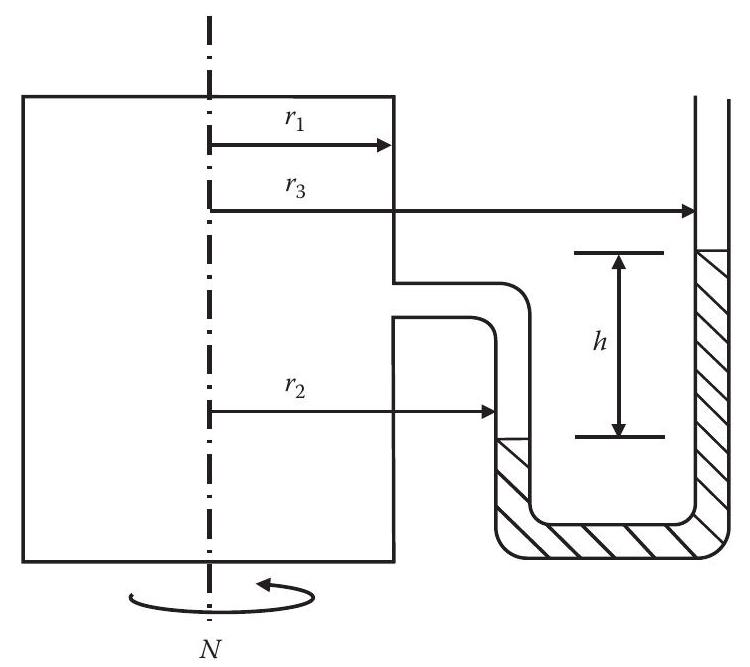
FIGURE P4.30 Revolving manometer.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781498724432
3rd Edition
Authors: Ron Darby, Raj P Chhabra
Question Posted:





