Refer to the scenario in Problem 47 regarding the identification of churning cellphone customers. Apply k-nearest neighbors
Question:
Refer to the scenario in Problem 47 regarding the identification of churning cellphone customers. Apply k-nearest neighbors to classify observations as churning or not by using Churn as the target (or response) variable. Set aside 20% of the data as a test set and use 80% of the data for training and validation.
a. Based on all the input variables, determine the value of k that maximizes the AUC in a validation procedure.
b. Remove DataPlan, RoamMins, OverageFee, and AccountWeeks from the set of input features considered and re-calibrate the value of k that maximizes the AUC.
How does this k-nearest neighbors model compare to the model obtained in part (a)?
c. For the best-performing k-nearest neighbors model in the validation procedure (with respect to AUC), compute and interpret the lift on the top 10% of test set observations most likely to churn.
Problem 47
Telecommunications companies providing cell-phone service are interested in customer retention. In particular, identifying customers who are about to churn (cancel their service) is potentially worth millions of dollars if the company can proactively address the reason that customer is considering cancellation and retain the customer. Data on past customers, some of whom churned and some who did not, have been collected. The variables in this data set are listed in the following table.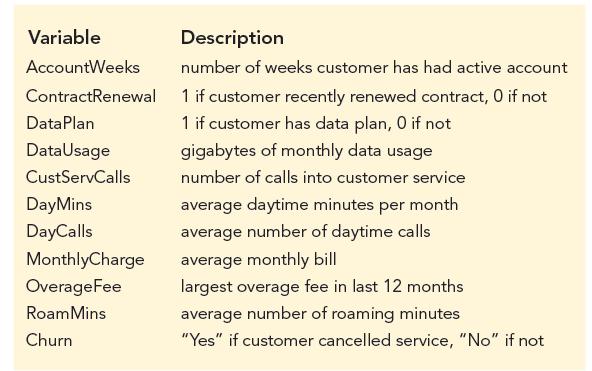
Apply logistic regression with lasso regularization to classify observations as churning or not by using Churn as the target (or response) variable. Set aside 20% of the data as a test set and use 80% of the data for training and validation.
Step by Step Answer:

Business Analytics
ISBN: 9780357902219
5th Edition
Authors: Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann





