Established in 1982, the German toy group Simba-Dickie realized a turnover of 616 million in 2018 (Spielwarenmesse,
Question:
Established in 1982, the German toy group Simba-Dickie realized a turnover of €616 million in 2018 (Spielwarenmesse, 2019). Although organic growth had a part to play, acquisition has been key to the company’s development, supported by a concentrated number of production centres and an extensive sales, marketing and warehousing network around the world. By 2019, the company had 20 toy brands in its portfolio, regional headquarters in France, Hong Kong and the United States, eight wholly owned production facilities in five different countries, production facilities in six different countries, subsidiaries in 23 and agencies in a further six countries
(see Table 11.4 for an indication of some of the group’s key brands, products and manufacturing locations). Few toy producers have global presence (think Hasbro, Lego and Mattel), and, as a medium-sized business, operating in this way allows Simba-Dickie to extend geographic market coverage for all its brands and, perhaps most importantly, to offer retailers an extensive product range (Simba-Dickie has in the region of 4000 products).
Germany, France, Italy and the UK represent the group’s most important market.
The majority of Simba-Dickie’s products are now produced in Europe, while the company’s Hong Kong office oversees subcontract manufacture in various Asian countries – irrespective of production location, the company’s automated storage and warehouse facility in Sonnenburg, Germany acts as the producer’s central logistics hub. Items produced in Europe might be shipped direct to retailers or to the group’s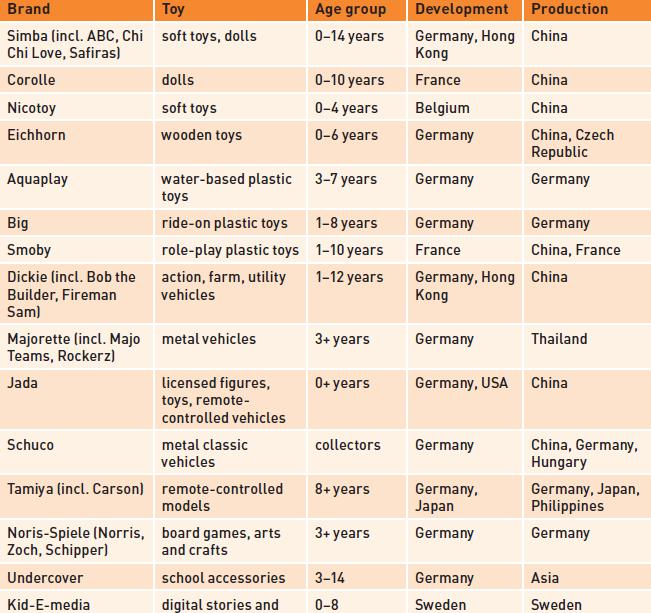
warehouse, while Chinese production and delivery to Simba-Dickie’s distribution network are coordinated by the group’s offices in Hong Kong and sales headquarters in Fürth. So, for example, in scheduling deliveries from China to Simba-Dickie’s logistics centre in Sonnenberg, planners have to factor in the production time as well as the 25 days it takes for shipments to reach Germany.
QUESTIONS
1. Based on the information in the case study, outline the structure of the supply chain of which Simba-Dickie is a part, identifying the key parties and their role in the supply of products to end-consumers.
2. Describe what you consider to be the main elements of the logistics service programme that retailers expect of Simba-Dickie. Do the locations of the toy producer’s activities present it with any difficulties in meeting these expectations?
3. Using the case study, and additional internet research, identify the principal differences in the distribution structure of the toy industry in France, Germany and the UK. What are the key implications of these differences for toy producers wanting to sell their products in these countries?
Step by Step Answer:

Business To Business Marketing
ISBN: 9781526494399,9781529726176
5th Edition
Authors: Ross Brennan , Louise Canning , Raymond McDowell





