Question: Let (mathbf{F}=leftlangle-x^{2} y, x, 0ightangle). Referring to Figure 19 , let (C) be the closed path (A B C D). Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate
Let \(\mathbf{F}=\left\langle-x^{2} y, x, 0ightangle\). Referring to Figure 19 , let \(C\) be the closed path \(A B C D\). Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate \(\int_{C} \mathbf{F} \cdot d \mathbf{r}\) in two ways. First, regard \(C\) as the boundary of the rectangle with vertices \(A, B, C\), and \(D\). Then treat \(C\) as the boundary of the wedge-shaped box with an open top.
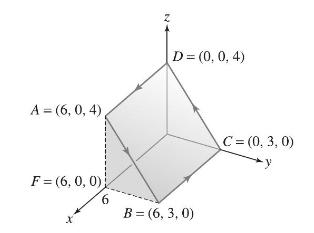
A = (6, 0, 4) F=(6, 0, 0); 6 z D=(0, 0, 4) B= (6, 3,0) C=(0, 3, 0)
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Stokes theorem connects a surface integral over a vector field to a line integral over the boundary of the surface Specifically it states that int intS abla times mathbfF cdot dmathbfS ointC mathbfF c... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


