Question: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate (iint_{mathcal{S}} mathbf{F} cdot d mathbf{S}) for the given vector field and surface. (mathbf{F}(x, y, z)=leftlangle x y z+x y,
Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate \(\iint_{\mathcal{S}} \mathbf{F} \cdot d \mathbf{S}\) for the given vector field and surface.
\(\mathbf{F}(x, y, z)=\left\langle x y z+x y, \frac{1}{2} y^{2}(1-z)+e^{x}, e^{x^{2}+y^{2}}ightangle, \mathcal{S}\) is the boundary of the solid bounded by the cylinder \(x^{2}+y^{2}=16\) and the planes \(z=0\) and \(z=y-4\).
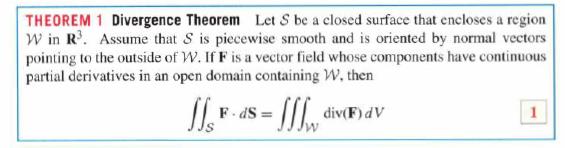
THEOREM 1 Divergence Theorem Let S be a closed surface that encloses a region W in R. Assume that S is piecewise smooth and is oriented by normal vectors pointing to the outside of W. If F is a vector field whose components have continuous partial derivatives in an open domain containing W, then 1 - Sw div(F) dv F-dS=
Step by Step Solution
3.58 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral iintmathcalS mathbfF cdot dmathbfS where mathcalS is the boundary of the solid bounded ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


