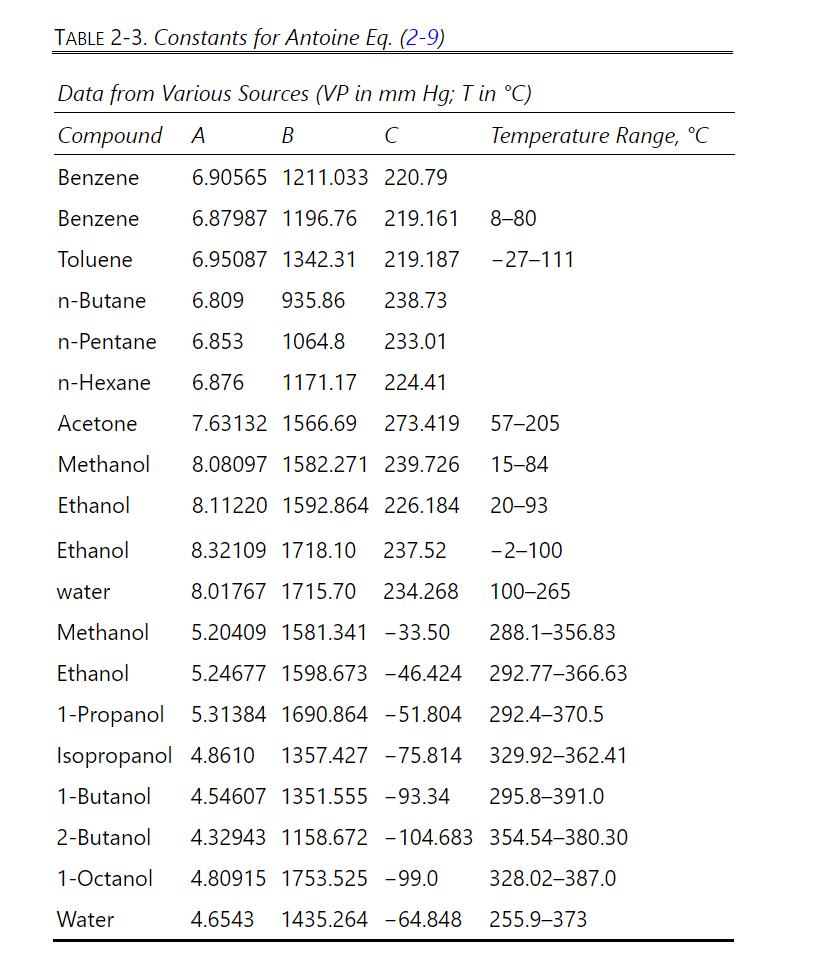
Antoine constants for vapor pressure for (mathrm{n})-pentane and (mathrm{n})-hexane are listed in Table 2-3. a. Predict the
Question:
Antoine constants for vapor pressure for \(\mathrm{n}\)-pentane and \(\mathrm{n}\)-hexane are listed in Table 2-3.
a. Predict the vapor pressure at \(0.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) for pure \(\mathrm{n}\)-pentane.
b. Predict the boiling point of pure \(\mathrm{n}\)-pentane at \(3.0 \mathrm{~atm}\) pressure.
c. Predict the boiling pressure if pure n-pentane is boiling at \(0.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
d. At a pressure of \(500.0 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\) and temperature of \(30.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), predict the \(\mathrm{K}\) values for \(\mathrm{n}\)-pentane and \(\mathrm{n}\)-hexane using Raoult's law.
e. If \(\mathrm{T}=30.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(\mathrm{p}=500.0 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\), determine the mole fractions in the liquid and vapor phases of an equilibrium mixture of \(n\)-pentane and \(n\) hexane.
f. 1.0 moles of a mixture that is \(75.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-pentane and \(25.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}-\) hexane is placed in a closed chamber. The pressure is adjusted to \(500.0 \mathrm{~mm}\) \(\mathrm{Hg}\), and the temperature to \(30.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The vapor and liquid mole fractions were found in part
e. How many moles of liquid and moles of vapor are there at equilibrium?
g. If \(1.0 \mathrm{~mol} / \mathrm{min}\) of a mixture that is \(75.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-pentane and \(25.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}-\) hexane is fed continuously to an equilibrium flash chamber operating at \(30.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(500.0 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\), find the flow rates of the liquid and vapor products.
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





