Determine the number of equilibrium stages needed for separation of light hydrocarbons in a stripping column by
Question:
Determine the number of equilibrium stages needed for separation of light hydrocarbons in a stripping column by stepping off stages and doing a dew- or bubble-point calculation at each stage. The \(100.0 \mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\) of saturated liquid feed at \(7.0 \mathrm{bar}\) is \(35.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-butane, \(45.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-pentane, and \(20.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) n-hexane. The column is at 7.0 bar, has a partial reboiler, and CMO can be used. The bottoms product is \(98.2 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-hexane and \(\approx / \mathrm{B}=19.0\). Make an appropriate assumption about distribution of the components, solve the mass balances, and determine \(\mathrm{B}, \mathrm{D}\), and mole fractions of distillate and bottoms products. Use either DePriester charts or Eq. (2-28) to step off stages. Report the temperature of each stage and the vapor and liquid mole fractions leaving each stage. Use of Table 2-5 constants in a spreadsheet to do dew- or bubblepoint calculations will probably save you time.
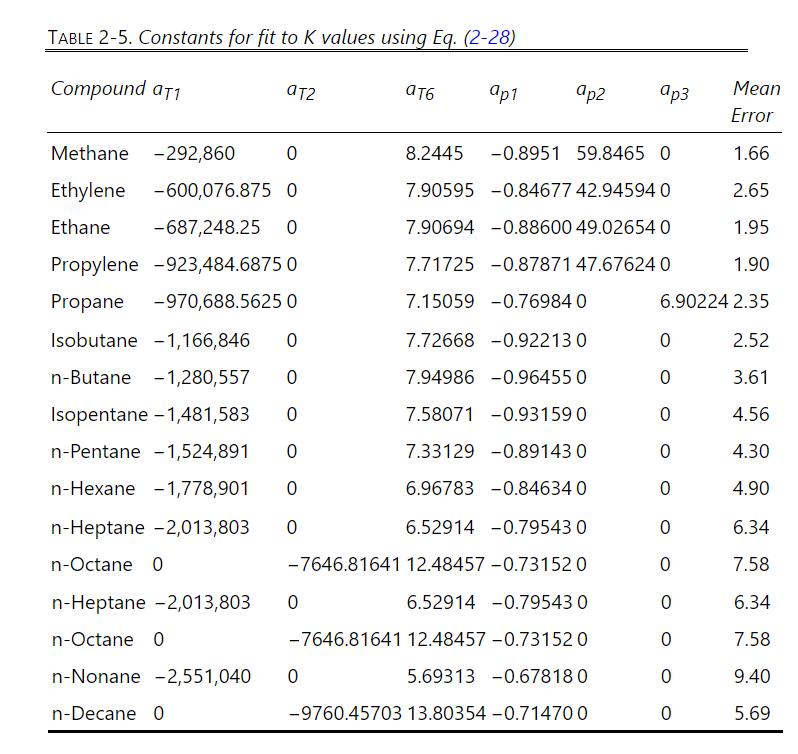
Equation 2-28
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





