The free-fall terminal velocity u (cm/s) of spherical water droplets in quiet air at 298 K and
Question:
The free-fall terminal velocity u (cm/s) of spherical water droplets in quiet air at 298 K and 1 atm is given approximately by:
u = 3,930 × D where D is the droplet diameter in cm. The mass transfer coefficient at the droplet-air interface can be predicted from the following approximate correlation:
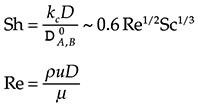
Assume that a droplet initially 0.3 cm in diameter falls in quiet, air at 298 K, 1 atm, and 40% relative humidity and that it can be treated as isotherm.
(a) Write down an explicit expression to predict the rate of evaporation from the droplet (mol/s) as a function of the droplet diameter D. (b)
Calculate the mass transfer coefficient when the droplet diameter is 0.3 cm.
(c) Calculate the initial rate of evaporation of water (mol/s) when the droplet diameter is 0.3 cm.
(d) Derive an ordinary differential equation relating the droplet diameter D to time.
(e) Integrate your equation in (d)
and determine the time required for the falling droplet to attain a diameter of 0.1 cm.
Step by Step Answer:

Heat And Mass Transfer For Chemical Engineers Principles And Applications
ISBN: 9781264266678
1st Edition
Authors: Giorgio Carta





