Use a process simulator to completely solve Example 6-1. Do not assume CMO. Compare temperature and mole
Question:
Use a process simulator to completely solve Example 6-1. Do not assume CMO. Compare temperature and mole fractions on each stage to the values obtained in Example 6-1 after one trial.
Example 6-1
A distillation column with a partial reboiler and a total condenser is separating nC4, nC5, and nC8. The column has two equilibrium stages (a total of three equilibrium contacts), and the feed is a saturated liquid fed into the bottom stage of the column. The column operates at 2.0 atm. The feed rate is 1000.0 kmol/h. zC4 = 0.20, zC5 = 0.35, zC8 = 0.45 (mole fractions). The reflux is a saturated liquid, and L/D = 1.5. The distillate rate is D = 550 kmol/h. Assume CMO. Use the DePriester charts or Eq. (2-28) for K values. For the first guess, assume that the temperatures on all stages and in the reboiler are equal to the feed bubble-point temperature. Use a matrix to solve the mass balances. Use bubble-point calculations for one iteration toward a solution for stage compositions and to predict new temperatures that could be used for a second iteration. Report the compositions on each stage and in the reboiler and the temperature of each stage and the reboiler.
Equation 2-28
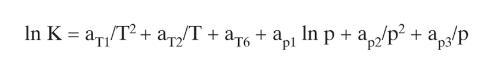
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





