Radiative forcing, R, measures the influence of carbon dioxide in altering the additional solar radiation trapped in
Question:
Radiative forcing, R, measures the influence of carbon dioxide in altering the additional solar radiation trapped in Earth’s atmosphere. The International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 1990 estimated k to be 6.3 in the radiative forcing equation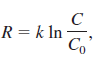
where C0 is the preindustrial amount of carbon dioxide and C is the current level.
(a) Use the equation R = 6.3 ln C/C0 to determine the radiative forcing R (in watts per square meter to the nearest tenth) expected by the IPCC if the carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere doubles from its preindustrial level.
(b) Determine the global temperature increase T, to the nearest tenth, that the IPCC predicted would occur if atmospheric carbon dioxide levels were to double, given T(R) = 1.03R.
Step by Step Answer:

College Algebra
ISBN: 978-0134697024
12th edition
Authors: Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels





