Calculate the Reynolds number for flow in the needle considered in Example 12.8 to verify the assumption
Question:
Calculate the Reynolds number for flow in the needle considered in Example 12.8 to verify the assumption that the flow is laminar. Assume that the density of the saline solution is 1025 kg/m3.
Strategy
We have all of the information needed, except the fluid speed U, which can be calculated from v̅ = Q/A = 1.70 m/s (verification of this is in this chapter's Problems and Exercises).
Data given in Example 12.8
An intravenous (IV) system is supplying saline solution to a patient at the rate of 0.120 cm3/s through a needle of radius 0.150 mm and length 2.50 cm. What pressure is needed at the entrance of the needle to cause this flow, assuming the viscosity of the saline solution to be the same as that of water? The gauge pressure of the blood in the patient's vein is 8.00 mm Hg. (Assume that the temperature is 20°C.)
Strategy
Assuming laminar flow, Poiseuille’s law applies. This is given by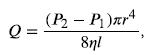
where P2 is the pressure at the entrance of the needle and P1 is the pressure in the vein. The only unknown is P2.
Step by Step Answer:






