Question: In this exercise, we will look at the different ways capacity affects overall performance. In general, cache access time is proportional to capacity. Assume that
In this exercise, we will look at the different ways capacity affects overall performance. In general, cache access time is proportional to capacity. Assume that main memory accesses take 70 ns and that memory accesses are 36% of all instructions.
The following table shows data for L1 caches attached to each of two processors, P1 and
P2.
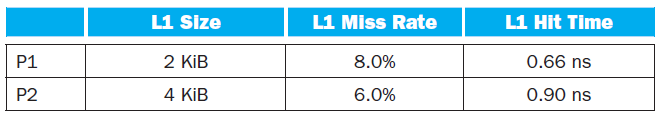
1. Assuming that the L1 hit time determines the cycle times for P1 and P2, what are their respective clock rates?
2. What is the Average Memory Access Time for P1 and P2?
3. Assuming a base CPI of 1.0 without any memory stalls, what is the total CPI for P1 and P2? Which processor is faster? For the next three problems, we will consider the addition of an L2 cache to P1 to presumably make up for its limited L1 cache capacity. Use the L1 cache capacities and hit times from the previous table when solving these problems. Th e L2 miss rate indicated is its local miss rate.
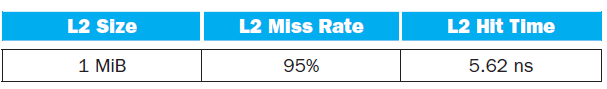
4. What is the AMAT for P1 with the addition of an L2 cache? Is the AMAT better or worse with the L2 cache?
5. Assuming a base CPI of 1.0 without any memory stalls, what is the total CPI for P1 with the addition of an L2 cache?
6. Which processor is faster, now that P1 has an L2 cache? If P1 is faster, what miss rate would P2 need in its L1 cache to match P1€™s performance? If P2 is faster, what miss rate would P1 need in its L1 cache to match P2€™s performance?
L1 Miss Rate L1 Size L1 Hit Time P1 0.66 ns 0.90 ns 2 KB 8.0% P2 4 KB 6.0% L2 Size L2 Miss Rate L2 Hit Time 1 MB 95% 5.62 ns
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 P1 152 GHz P2 111 GHz 2 P1 631 ns 956 cycles P2 511 ns 568 cycles ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


