Question: The following three problems in this Exercise refer to a function f that calls another function func. The code for C function func is already
The following three problems in this Exercise refer to a function f that calls another function func. The code for C function func is already compiled in another module using the MIPS calling convention from Figure 2.14. The function declaration for func is “int func(int a, int b);”. The code for function f is as follows:
Figure 2.14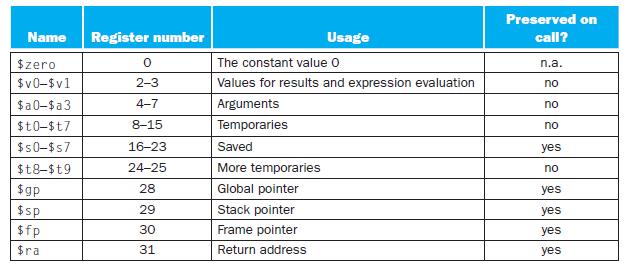

we use the tail-call optimization in this function? If no, explain why not. If yes, what is the difference in the number of executed instructions in f with and without the optimization?
Name Register number $zero $v0-$vl $a0-$a3 $t0-$t7 $50-$s7 $t8-$t9 $gp $sp $fp $ra 0 2-3 4-7 8-15 16-23 24-25 28 29 30 31 The constant value 0 Values for results and expression evaluation Arguments Temporaries Usage Saved More temporaries Global pointer Stack pointer Frame pointer Return address Preserved on call? n.a. no no no yes no yes yes yes yes
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets examine each function in turn to see if tailcall optimization may be used for the provided functions f a return funcfuncab cd int fint a int b int c int d b int fint a int b int c int d return fu... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


