Question: The importance of having a good branch predictor depends on how oft en conditional branches are executed. Together with branch predictor accuracy, this will determine
The importance of having a good branch predictor depends on how oft en conditional branches are executed. Together with branch predictor accuracy, this will determine how much time is spent stalling due to mispredicted branches. In this exercise, assume that the breakdown of dynamic instructions into various instruction categories is as follows:
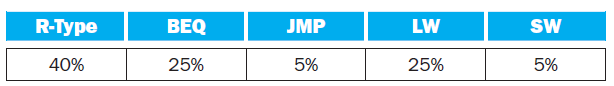
Also, assume the following branch predictor accuracies:
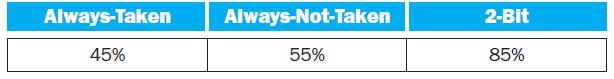
1. Stall cycles due to mispredicted branches increase the CPI. What is the extra CPI due to mispredicted branches with the always-taken predictor? Assume that branch outcomes are determined in the EX stage, that there are no data hazards, and that no delay slots are used.
2. Repeat 4.15.1 for the €œalways-not-taken€ predictor.
3. Repeat 4.15.1 for for the 2-bit predictor.
4. With the 2-bit predictor, what speedup would be achieved if we could convert half of the branch instructions in a way that replaces a branch instruction with an ALU instruction? Assume that correctly and incorrectly predicted instructions have the same chance of being replaced.
5. With the 2-bit predictor, what speedup would be achieved if we could convert half of the branch instructions in a way that replaced each branch instruction with two ALU instructions? Assume that correctly and incorrectly predicted instructions have the same chance of being replaced.
6. Some branch instructions are much more predictable than others. If we know that 80% of all executed branch instructions are easy-to-predict loop-back branches that are always predicted correctly, what is the accuracy of the 2-bit predictor on the remaining 20% of the branch instructions?
BEQ R-Type JMP LW SW 5% 40% 25% 5% 25% Always-Taken Always-Not-Taken 2-Bit 45% 55% 85%
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Each branch that is not correctly predicted by the alwaystaken predictor ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


