Question: A dc-dc converter is a device that takes as an input an unregulated dc voltage and provides a regulated dc voltage as its output. The
A dc-dc converter is a device that takes as an input an unregulated dc voltage and provides a regulated dc voltage as its output. The output voltage may be lower (buck converter), higher (boost converter), or the same as the input voltage. Switching dc-dc converters have a semiconductor active switch (BJT or FET) that is closed periodically with a duty cycle d in a pulse width modulated (PWM) manner. For a boost converter, averaging techniques can be used to arrive at the following state equations (Van Dijk, 1995):
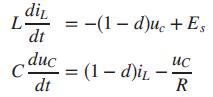
where L and C are, respectively, the values of internal inductance and capacitance; iL is the current through the internal inductor; R is the resistive load connected to the converter; Es is the dc input voltage; and the capacitor voltage, uC, is the converter’s output.
a. Write the converter’s equations in the form
ẋ = Ax + Bu
y = Cx
assuming d is a constant.
b. Using the A, B, and C matrices of Part a, obtain the converter’s transfer function UC(s)/Es(s).
dir L = -(1 - d)u. + E, dt duc C 3 (1- d)i dt R
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


