(Master budget preparation; advanced) Color Blaze Company manufactures a red industrial dye. The company is preparing its...
Question:
(Master budget preparation; advanced) Color Blaze Company manufactures a red industrial dye. The company is preparing its 2006 master budget and has presented you with the following information.
1. The December 31, 2005, balance sheet for the company follows.
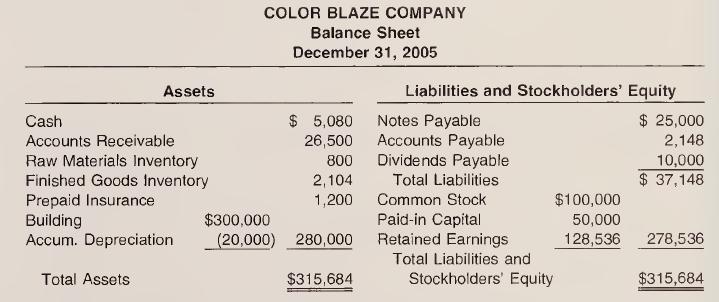
2. The Accounts Receivable balance at 12/31/05 represents the remaining balances of November and December credit sales. Sales were $70,000 and $65,000, respectively, in those two months.
3. Estimated sales in gallons of dye for January through May 2006 follow.

Each gallon of dye sells for $12.
4. The collection pattern for accounts receivable is as follows: 70 percent in the month of sale, 20 percent in the first month after the sale, and 10 percent in the second month after the sale. Color Blaze expects no bad debts and gives no cash discounts.
5. Each gallon of dye has the following standard quantities and costs for direct materials and direct labor:

Variable overhead (VOH) is applied to the product on a machine-hour basis. Processing 1 gallon of dye takes 5 hours of machine time. The variable overhead rate is $0.06 per machine hour; VOH consists entirely of utility costs. Total annual fixed overhead is $120,000; it is applied at $1 per gallon based on an expected annual capacity of 120,000 gallons. Fixed overhead per year is composed of the following costs:

Fixed overhead is incurred evenly throughout the year.
6. There is no beginning inventory of work in process. All work in process is completed in the period in which it is started. Raw materials inventory at the beginning of the year consists of 1,000 gallons of direct material at a standard cost of $0.80 per gallon. There are 400 gallons of dye in finished goods inventory at the beginning of the year carried at a stan¬ dard cost of $5.26 per gallon: direct material, $0.96; direct labor, $3.00; variable overhead, $0.30; and fixed overhead, $1.00.
7. Accounts Payable relates solely to raw material and is paid 60 percent in the month of purchase and 40 percent in the month after purchase. No discounts are given for prompt payment.
8. The dividend will be paid in January 2006.
9. A new piece of equipment costing $9,000 will be purchased on March 1, 2006. Payment of 80 percent will be made in March and 20 percent in April. The equipment has a useful life of three years and will have no salvage value.
10. The note payable has a 12 percent interest rate; interest is paid at the end of each month. The principal of the note is repaid as cash is avail¬ able to do so.
11. Color Blaze’s management has set a minimum cash balance at $5,000. Investments and borrowings are made in even $100 amounts. Invest¬ ments will earn 9 percent per year.
12. The ending finished goods inventory should include 5 percent of the next month's needs. This is not true at the beginning of 2006 due to a miscalculation in sales for December. The ending inventory of raw mate¬ rials also should be 5 percent of the next month’s needs.
13. Selling and administrative costs per month are as follows: salaries, $18,000; rent, $7,000; and utilities, $800. These costs are paid in cash as they are incurred.
Prepare a master budget for each month of the first quarter of 2006 and pro forma financial statements as of the end of the first quarter of 2006.
Step by Step Answer:

Cost Accounting Foundations And Evolutions
ISBN: 9780324235012
6th Edition
Authors: Michael R. Kinney, Jenice Prather-Kinsey, Cecily A. Raiborn





