Comprehensive Review of Variances, Mix Variances, Analysis of Differences between Budget and Actual: Sip-Fizz Bottling Company prepared
Question:
Comprehensive Review of Variances, Mix Variances, Analysis of Differences between Budget and Actual: Sip-Fizz Bottling Company prepared a sales and production budget for the 48-ounce bottle. 12-ounce can, and 10-ounce bottle units that the company produces and sells. Unit variable costs per case of soda are calculated as follows:
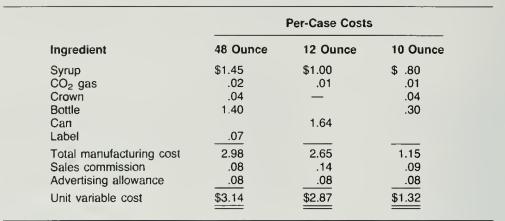
The advertising allowance is based on the number of cases sold. The selling price for the 48-ounce case is $5.40; for the 12-ounce case. $4.35; and for the 10-ounce case, $2.80. Sales for the month of November were forecasted at 70,000 cases of the 48-ounce bottles: 60,000 cases of 12-ounce cans; and 110,000 cases of 10-ounce bottles. Fixed costs were estimated at $175,000. During November, actual sales amounted to 80,000 cases of 48-ounce bottles, 50,000 cases of 12-ounce cans, and 120,000 cases of 10-ounce bottles. Actual and budgeted selling prices were equal. Syrup costs were 10 percent greater than ex- pected, but all other costs were at the same per-unit amount as indicated above. Total fixed costs, which are all other costs not explicitly identified above, amounted to $182,000.
The company uses variable costing for internal reporting purposes. There were no beginning and ending inventories.
Required:
a. Determine the budgeted and actual operating profits.
b. Explain the difference between the budgeted and actual net operating profits in as much detail as possible.
Step by Step Answer:






