Question: Suppose we apply graph convolutional networks (GCNs) on grid-like graphs (e.g., images) without normalizing adjacency matrix (i.e., removing Steps 2-3 in Fig. 10.38). Explain why
Suppose we apply graph convolutional networks (GCNs) on grid-like graphs (e.g., images) without normalizing adjacency matrix (i.e., removing Steps 2-3 in Fig. 10.38). Explain why it is essentially a 2 -D convolution with a special type of filters.
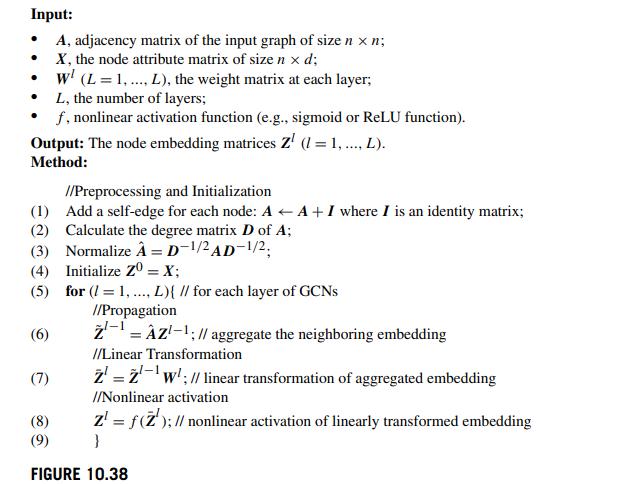
Input: A, adjacency matrix of the input graph of size n x n; X, the node attribute matrix of size n x d; w (L= 1,..., L), the weight matrix at each layer; L, the number of layers; f, nonlinear activation function (e.g., sigmoid or ReLU function). . Output: The node embedding matrices Z (1 = 1, ..., L). Method: //Preprocessing and Initialization (1) Add a self-edge for each node: A A+ I where I is an identity matrix; (2) Calculate the degree matrix D of A; (3) Normalize = D-1/2AD-1/2, (4) Initialize z0 = X; (5) for (/= 1,..., L){ // for each layer of GCNs //Propagation (6) (7) -AZ-1: // aggregate the neighboring embedding = //Linear Transformation 2 2w; // linear transformation of aggregated embedding //Nonlinear activation z = f(2'); // nonlinear activation of linearly transformed embedding } (8) (9) FIGURE 10.38
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Suppose the dimensions of input feature map and output feature map are p q respectively then t... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


