Wolbachia is a microbial symbiont estimated to be hosted by about (40 %) of all arthropod species,
Question:
Wolbachia is a microbial symbiont estimated to be hosted by about \(40 \%\) of all arthropod species, transmitted primarily from females to their offspring through the eggs. Researchers conducted a study on a wasp species to understand the effect of Wolbachia on the lifetime reproductive success of an insect host. They estimated the realized lifetime reproductive success of female wasps by collecting them soon after they die naturally in the field, counting the number of eggs remaining in their ovaries and quantifying Wol bachia density in their body.
In the first stage of the experiment, researchers estimated potential reproductive success by collecting female wasps as they emerged from eggs then dissecting them to count the number of eggs in their ovaries. These data were used to create a predictive model for initial number of eggs based on tibia length (an indicator of body size) and Wolbachia density. Tibia length was measured in \(\mu \mathrm{m}\), and Wolbachia density in units of -ddCt.
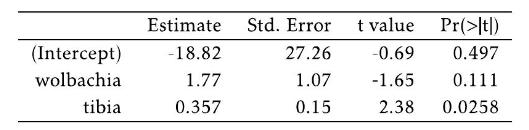
(a) Write the model equation.
(b) Interpret the model coefficients in the context of the data.
(c) Predict mean initial egg count for a wasp with tibia length of \(171.4286 \mu \mathrm{m}\) and Wolbachia density of -3.435 \(-\mathrm{ddCt}\).
Step by Step Answer:

Introductory Statistics For The Life And Biomedical Sciences
ISBN: 9781943450121
1st Edition
Authors: Julie Vu, David Harrington





