Question: Determine the finite population correction factor for each value of N and n. (a) N = 1000 and n = 500 (b) N = 1000
Determine the finite population correction factor for each value of N and n.
(a) N = 1000 and n = 500
(b) N = 1000 and n = 100
(c) N = 1000 and n = 75
(d) N = 1000 and n = 50
(e) N = 100 and n = 50
(f) N = 400 and n = 50
(g) N = 700 and n = 50
(h) N = 1200 and n = 50
What happens to the finite population correction factor as the sample size n decreases but the population size N remains the same? as the population size N increases but the sample size n remains the same?
Use the information below.
In this section, you studied the construction of a confidence interval to estimate a population mean. In each case, the underlying assumption was that the sample size n was small in comparison to the population size N. When n ≥ 0.05N, however, the formula that determines the standard error of the mean σx needs to be adjusted, as shown below.
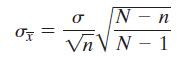
Recall from the Section 5.4 exercises that the expression √(N - n)/(N - 1) is called a finite population correction factor. The margin of error is
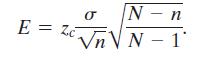
N-n Vn V N 1
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Given N1000 n 500 Now FCR NnN1 FCR 100050010001 FCR 070 b ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


