Using the Nernst equation and the ion concentrations given in Table 121, calculate the equilibrium membrane potential
Question:
Using the Nernst equation and the ion concentrations given in Table 12–1, calculate the equilibrium membrane potential of K+ and Na+ that is, the membrane potential where there would be no net movement of the ion across the plasma membrane (assume that the concentration of intracellular Na+ is 10 mM). What membrane potential would you predict in a resting animal cell? Explain your answer. What would happen if a large number of Na+ channels suddenly opened, making the membrane much more permeable to Na+ than to K+?
What would you predict would happen next if the Na+ channels closed again?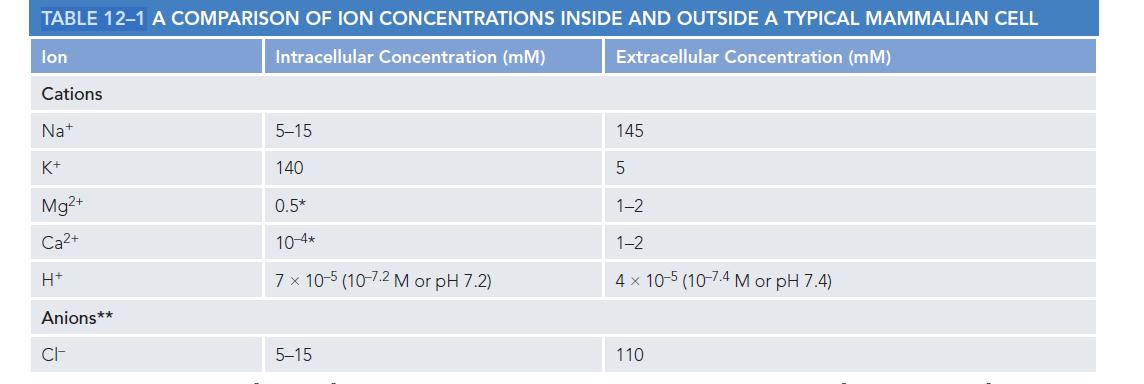
Step by Step Answer:

Essential Cell Biology
ISBN: 9780393680362
5th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Karen Hopkin, Alexander Johnson, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter





