Photovoltaic (PV) cells convert sunlight energy directly into electricity, with no moving parts (recall Fig. 37.21). In
Question:
Photovoltaic (PV) cells convert sunlight energy directly into electricity, with no moving parts (recall Fig. 37.21). In a PV cell, photons incident on a semiconductor PN junction promote electrons to the conduction band, producing electron-hole pairs and driving current through an external circuit (Fig. 37.26). Commercially available PV cells are 15–20% efficient, meaning they convert this fraction of incident sunlight into electrical energy; the theoretical maximum efficiency is around 33% for silicon-based PV cells. An important limitation on PV efficiency is the relation between the solar spectrum and PV cells’ semiconductor band-gap energy. For silicon, the band gap is 1.14 eV; photons with less energy can’t promote electrons to the conduction zone and are thus unavailable for the PV energy conversion. Conversely, photons with more than the band-gap energy give up their excess energy as heat, also reducing PV efficiency.
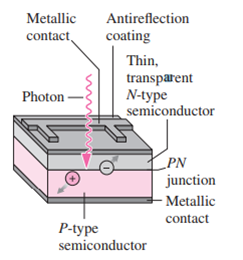
Problem 53 shows that the median wavelength in the solar spectrum is 710 nm, at the visible-IR boundary. What percentage of the incident solar energy can a silicon PV cell absorb?
a. about 25%
b. about 50%
c. about 75%
Step by Step Answer:






