In addition to common?size financial statements, common?base year financial statements are often used. Common?base year financial statements
Question:
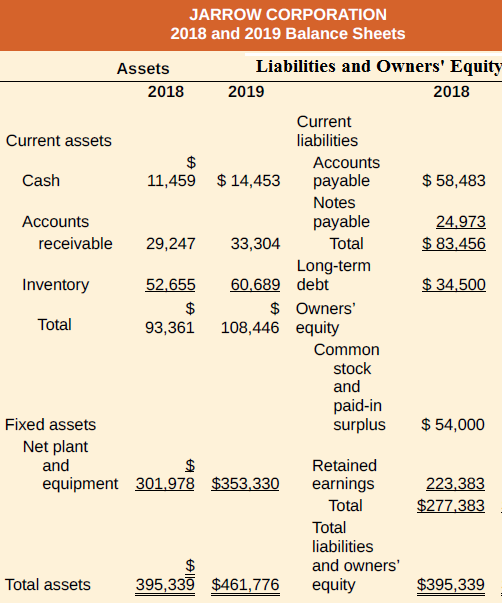
In addition to common?size financial statements, common?base year financial statements are often used. Common?base year financial statements are constructed by dividing the current year account value by the base year account value. The result shows the growth rate in the account. Using the following financial statements, construct the common-size balance sheet and common?base year balance sheet for the company. Use 2018 as the base year.
Use the following information for Problems 19, 20, and 22: The discussion of EFN in the chapter implicitly assumed that the company was operating at full capacity. Often, this is not the case. Assume that Rosengarten was operating at 90 percent capacity. Fullcapacity sales would be $1,000/.90 = $1,111. The balance sheet shows $1,800 in fixed assets. The capital intensity ratio for the company is:
Capital intensity ratio = Fixed assets/Full-capacity sales = $1,800 / $1,111 = 1.62
This means that Rosengarten needs $1.62 in fixed assets for every dollar in sales when it reaches full capacity. At the projected sales level of $1,250, it needs $1,250 ? 1.62 = $2,025 in fixed assets, which is $225 lower than our projection of $2,250 in fixed assets. So, EFN is $565 - 225 = $340.
Financial StatementsFinancial statements are the standardized formats to present the financial information related to a business or an organization for its users. Financial statements contain the historical information as well as current period’s financial...
Step by Step Answer:

Corporate Finance
ISBN: 978-1259918940
12th edition
Authors: Stephen Ross, Randolph Westerfield, Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford Jordan





