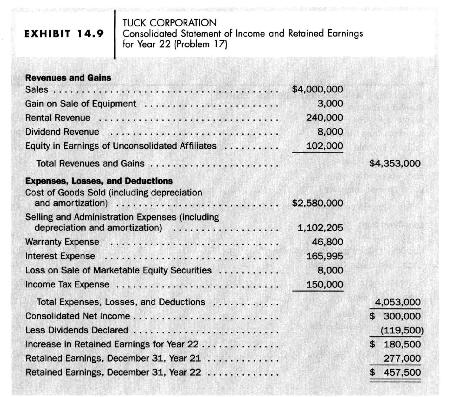
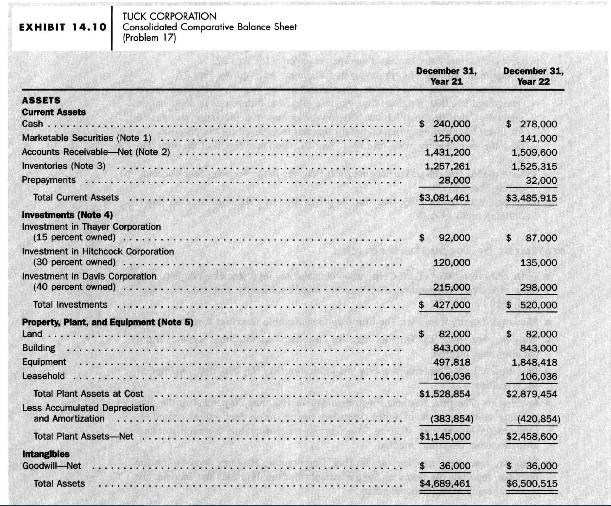
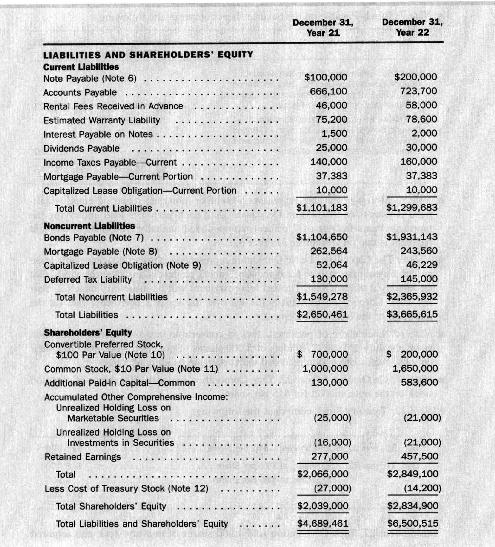
Comprehensive review problem. Exhibit 14.9 presents a consolidated statement of income and retained earnings for Year 22,
Question:
Comprehensive review problem. Exhibit 14.9 presents a consolidated statement of income and retained earnings for Year 22, and Exhibit 14.10 presents a consolidated balance sheet for Tuck Corporation as of December 31, Year 21 and Year 22. A statement of accounting policies and a set of notes to the financial statements appear below. After studying these financial statements and notes, respond to each of the following questions and calculation requirements.
a. Prepare an analysis that explains the change in the Marketable Equity Securities account during Year 22
b. Calculate the proceeds from sales of marketable equity securities classified as current assets during Year 22.
c. Calculate the amount of the estimated uncollectible accounts provision made during Year 22.
d. Calculate the amount of cost of goods sold assuming Tuck Corporation used a FIFO cost flow assumption.
e. Give the journal entry(s) to account for the change in the Investment in Thayer Corporation account during Year 22.
f. Calculate the amount of income or loss from the Investment in Thayer Corporation during Year 22.
g. Give the journal entry(s) to account for the change in the Investment in Davis Corporation account during Year 22.
h. Refer to Note 5. Give the journal entry to record the sale of equipment during Year 22.
i. Refer to Note 9. Demonstrate that the \(\$ 106,036\) is the correct amount of the leasehold asset at the beginning of the lease term.
j. Calculate the amount of cash received during Year 22 for rental fees.
k. Calculate the actual cost of goods and services required to service customers' warranties during Year 22.
1. Refer to Note 7. Calculate the amount of interest expense on the \(\$ 1\) million, 6 -percent bonds for Year 22.
m. Give the journal entry(s) for the change in the Mortgage Payable accounts during Year 22. Be sure to consider the current portion.
n. Verify that the book value of the combined current and noncurrent portions of the Capitalized Lease Obligation on December 31, Year 21, should be \(\$ 62,064\).
o. Prepare an analysis that explains the change in the book value of the combined current and noncurrent portions of the Capitalized Lease Obligation during Year 22.
p. Give the journal entry to record income tax expense for Year 22.
q. Compute the amount of cash payments for income taxes during Year 22.
r. The income tax rate is 30 percent. Assume that during Year 22, Tuck Corporation recognized \(\$ 12,000\) of deferred tax expense related to differences in depreciation methods. Calculate the difference between the amount of depreciation recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amount recognized for tax purposes.
s. Give the journal entry made on July 1 , Year 22, upon conversion of the preferred stock.
t. Give the journal entry(s) to account for the change in the Treasury Stock account during Year 22.
u. Prepare a T-account work sheet for the preparation of a statement of cash flows, defining funds as cash.
\section*{STATEMENT OF ACCOUNTING POLICIES}
- Basis of consolidation. Tuck Corporation consolidates its financial statements with those of Harvard Corporation, a 100-percent-owned subsidiary acquired on January 2, Year 20.
- Marketable equity securities. The firm reports marketable securities at market value.
- Accounts receivable. The firm accounts for customers' uncollectible accounts using the allowance method.
- Inventories. Tuck Corporation uses a last-in, first-out (LIFO) cost flow assumption for inventories.
- Investments. The firm accounts for investments of less than 20 percent of the outstanding common stock of other companies using the market value method. It accounts for investments of 20 to 50 percent of the outstanding common stock of affiliates using the equity method.
- Building, equipment, and leaseholds. Tuck Corporation calculates depreciation for financial reporting purposes using the straight-line method and for income tax reporting using MACRS depreciation.
- Goodwill. The firm does not amortize goodwill in accordance with FASB Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142.
- Interest expense on long-term debt. The firm measures interest expense on longterm debt using the effective interest method.
- Deferred income taxes. Tuck Corporation provides deferred income taxes for temporary differences between book and taxable income.
\section*{NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS}
- Note 1: The balance sheet presents marketable equity securities at market value, which is less than acquisition cost by \(\$ 25,000\) on December 31 , Year 21 , and \(\$ 21,000\) on December 31, Year 22. Tuck Corporation sold marketable equity securities costing \(\$ 35,000\) during Year 22. It received no dividends from marketable equity securities during Year 22.
- Note 2: The balance sheet presents accounts receivable net of an allowance for uncollectible accounts of \(\$ 128,800\) on December 31 , Year 21 , and \(\$ 210,400\) on December 31, Year 22. Tuck Corporation wrote off a total of \(\$ 63,000\) of accounts receivable as uncollectible during Year 22.
- Note 3: The valuation of inventories on a FIFO basis exceeded the amounts on a LIFO basis by \(\$ 430,000\) on December 31 , Year 21 , and by \(\$ 410,000\) on December 31, Year 22.
- Note 4: Davis Corporation reported net income for Year 22 of \(\$ 217,500\) and declared and paid dividends totaling \(\$ 60,000\) during the year. Tuck Corporation invested an additional \(\$ 20,000\) in Davis Corporation during Year 22, but its ownership percentage remained at 40 percent.
- Note 5: Tuck Corporation sold equipment with a cost of \(\$ 23,000\) and a book value of \(\$ 4,000\) during Year 22. This was the only disposition of property, plant, or equipment during the year.


During Year 22, Tuck Corporation sold 1,800 shares of treasury stock and acquired 550 shares.
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Accounting An Introduction To Concepts Methods And Uses
ISBN: 9780324183511
10th Edition
Authors: Clyde P. Stickney, Roman L. Weil





