Starr Mfg.'s predetermined overhead rate is (200 %) of direct labor. Information on the company's production activities
Question:
Starr Mfg.'s predetermined overhead rate is \(200 \%\) of direct labor. Information on the company's production activities during September follows.
a. Purchased raw materials on credit, \(\$ 125,000\).
b. Materials requisitions record use of the following materials for the month.
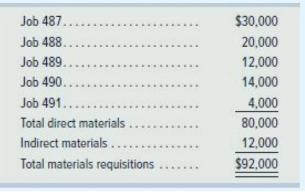
c. Time tickets record use of the following labor for the month. These wages are paid in cash.

d. Applied overhead to Jobs 487, 489, and 490.
e. Transferred Jobs 487, 489, and 490 to Finished Goods Inventory.
f. Sold Jobs 487 and 489 on credit for a total price of \(\$ 340,000\).
g. Recorded the cost of goods sold for Jobs 487 and 489 .
h. Incurred the following actual other overhead costs during the month.

i. Applied overhead at month-end to the Work in Process Inventory account (for Job 488 and Job 491) using the predetermined overhead rate of \(200 \%\) of direct labor cost.
Required
1. Prepare a job cost sheet for each job worked on in the month. Use the following simplified form.
 2. Prepare journal entries to record the events and transactions a through \(i\).
2. Prepare journal entries to record the events and transactions a through \(i\).
3. Set up T-accounts for each of the following accounts, each of which started the month with a zero balance: Raw Materials Inventory, Work in Process Inventory, Finished Goods Inventory, Factory Overhead, Cost of Goods Sold. Post the journal entries to these T-accounts and determine the ending balance of each account.
4. (a) Compute the total cost of each job in process and prove that the sum of their costs equals the Work in Process Inventory account balance. (b) Compute the total cost of each job finished but not sold, and prove that the sum of their costs equals the Finished Goods Inventory balance. (c) Compute the total cost of each job sold, and prove that the sum of their costs equals the Cost of Goods Sold balance.
Step by Step Answer:






