Armstrong Chemical began operations in January. The company manufactures an acrylic car wax called Tough-Coat. The following
Question:
Armstrong Chemical began operations in January. The company manufactures an acrylic car wax called Tough-Coat. The following standard cost estimates were developed several months before the company began operations, based on an estimated production of 1,000,000 units (pints).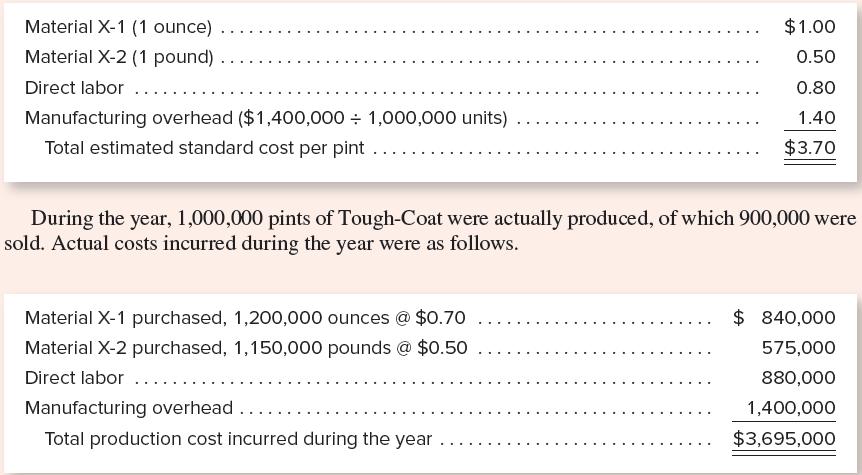
The company’s inventories at the end of the year consisted of the following, with the Finished Goods inventory stated at standard cost.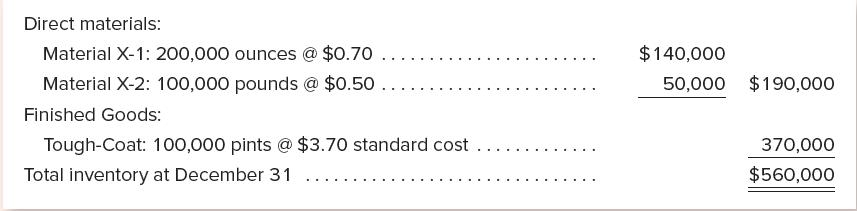
The independent certified public accountant who has been engaged to audit the company’s financial statements wants to adjust the valuation of Finished Goods inventory to “a revised standard cost” that would take into account the favorable price variance on material X-1 ($0.30 per ounce) and the 10 percent wage increase early in the year. (An unfavorable quantity variance on material X-2 was caused by spoilage in production; the CPA feels no adjustment to the standard should be made for this type of item.) The president of the company objects on the following grounds: “Such a revision is not necessary because the cost of material X-1 already shows signs of going up and the wage increase was not warranted because the productivity of workers did not increase one bit. Furthermore, if we revise our inventory figure of $560,000, our operating income will be reduced from the current level of $50,000.” You are called in by the president to help resolve the controversy.
Instructions
a. Do you agree with the president that revision of the $3.70 standard cost figure is not necessary?
b. Assume that you conclude that the standards for this first year of operations should be revised. Compute a “revised standard cost per unit” and determine the value to be assigned to the ending inventory of finished units using this revised standard cost.
c. What effect would this revaluation of Finished Goods inventory have on the company’s operating income?
d. Using the original standards, compute the following.
1. Materials price variance and quantity variance for material X-1.
2. Materials price variance and quantity variance for material X-2.
3. Total direct labor variance (do not separate into rate variance and usage variance).
4. Total manufacturing overhead variance.
Step by Step Answer:

Financial And Managerial Accounting The Basis For Business Decisions
ISBN: 9781260247930
19th Edition
Authors: Jan Williams, Susan Haka, Mark Bettner, Joseph Carcello





