As this chapter described, IAS 38 permits firms to capitalize development phase costs incurred on internal projects
Question:
As this chapter described, IAS 38 permits firms to capitalize “development phase” costs incurred on internal projects once technical feasibility and other criteria demonstrating the existence of an asset are met.
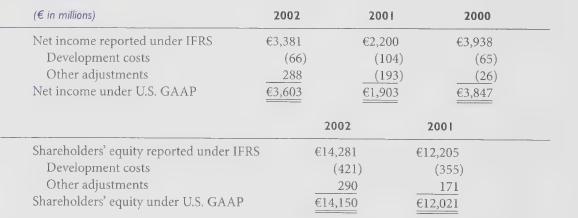
Nokia, the Finnish telecommunications giant, prepares its financial statements using IFRS and, consistent with the JAS 38 standard, capitalizes a range of product development costs.
Nokia lists its shares on the New York Stock Exchange and discloses the impact of capitalizing its various product development costs in the following U.S. GAAP reconciliation included with its Form 20-F filing. The reconciling item includes only nonsoftware development costs. Software development costs are capitalized under Nokia's application of both IFRS and U.S. GAAP.
Required:
1. Did Nokia’s capitalization of development costs increase or decrease IFRS net income relative to U.S. GAAP income during 2000 to 2002? Explain. Can you expect this relationship always to hold?
2. Did Nokia's capitalization of development costs increase or decrease IFRS shareholders’
equity relative to U.S. GAAP equity during 2001 and 2002? Explain. Can you expect this relationship always to hold?
3. List some reasons why a company’s management might capitalize development costs.
Step by Step Answer:






