GM first provided retiree health care benefits to UAW employees in 1961. In the fall of 2007,
Question:
GM first provided retiree health care benefits to UAW employees in 1961. In the fall of 2007, after a short strike, the UAW and GM reached an agreement to end that coverage. The key terms and effects of the agreement are as follows:
1. The agreement relates to approximately \($46.7\) billion of the \($64.3\) billion OPEB liability reported in its 2006 annual report.
2. GM would continue to take responsibility for retiree health benefits through 2010.
3. Between January 1, 2008 and January 1, 2010, GM will make \($13.5\) billion in cash payments to the UAW portion of GM’s existing VEBA trust (the UAW portion of trust assets was approximately \($16\) billion at the time of the agreement).
4. GM will issue to the VEBA trust a convertible note for \($4.327\) billion (approximate maturity date, January 1, 2013).
5. GM will have a two-tier wage structure.
6. Pension benefits will be improved, thereby resulting in an increase of \($4.3\) billion in GM's pension PBO.
7. On January 1, 2010, GM will transfer the UAW portion of its VEBA trust to a new UAW-controlled VEBA trust, and the UAW will assume responsibility for UAW-related retiree health benefits.
8. GM may be required to make up to \($1.575\) billion in additional payments if the VEBA trust experiences significant shortfalls.
9. The UAW may not negotiate further for retiree health care benefits.
10. Upon the transfer of its UAW-related retiree health benefits, GM plans to recognize a negative plan amendment of approximately \($22\) billion.
11. Other key elements relate to cost-of-living adjustments, outsourcing, and job security.
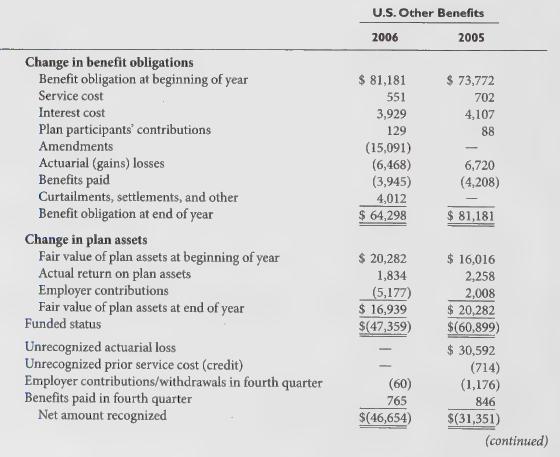
Information related to its 2006 annual report includes the following:

The 2006 annual report also provides the following information related to GM’s OPEB plans.
GM also provides post-employment extended disability benefits comprised of income security, health care, and life insurance to U.S. and Canadian employees who become disabled and can no longer actively work. The cost of such benefits is recognized during the period employees provide service. ...
GM contributes to its U.S. hourly and salaried Voluntary Employees Beneficiary Association (VEBA) trusts for OPEB plans. There were no contributions made by GM to the VEBA trust during 2006 and 2005. Contributions by participants to the other OPEB plans were \($129\) million, \($89\) million, and \($87\) million for 2006, 2005, and 2004, respectively. GM withdrew a total of \($4.1\) billion and \($3.2\) billion from plan assets of its VEBA trusts for OPEB plans in 2006 and 2005, respectively.
GM uses a December 31 measurement date for the majority of its U.S. pension plans and a September 30 measurement date for U.S. OPEB plans.

The components of pension and OPEB expense along with the assumptions used to determine benefit obligations are as follows:
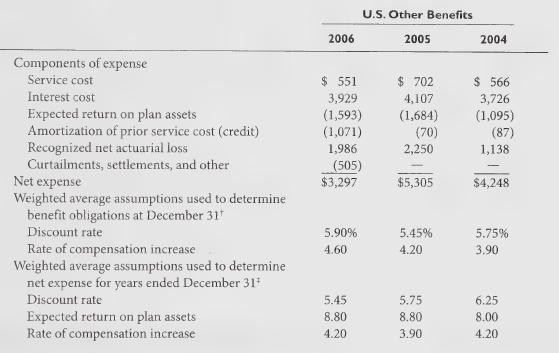
Determined as of end of year.
Determined as of beginning of year. Appropriate discount rates were used during 2006 to measure the effects of curtailments and plan amendments on various plans.
The following are estimated amounts to be amortized from AOCTI into net periodic benefit cost during 2007 based on December 31, 2006 and January 1, 2007 plan meastirements (dollars in millions):

On February 7, 2006, GM announced it would increase the U.S. salaried workforce’s participation in the cost of health care, capping GM’s contributions to salaried retiree health care at the level of 2006 expenditures. The remeasurement of the U.S. salaried OPEB plans as of February 9, 2006 as a result of these benefit modifications generated a \($0.5\) billion reduction in OPEB expense for 2006 and is reflected in the components of expense table above. This remeasurement reduced the U.S. accumulated postretirement benefit obligation (APBO) by \($4.7\) billion.
Effective March 31, 2006, the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan approved the tentative settlement agreement with the UAW (UAW Settlement Agreement) related to reductions in hourly retiree health care; this approval is now under appeal. . .. GM accounted for the reduced health care coverage provisions of the UAW Settlement Agreement as an amendment of GM’s Health Care Program for Hourly Employees (Modified Plan). ... The Modified Plan APBO reduction of \($17.4\) billion is being amortized on a straight-line basis over the remaining service lives of active UAW hourly employees (7.4 years) as a reduction of OPEB expense.
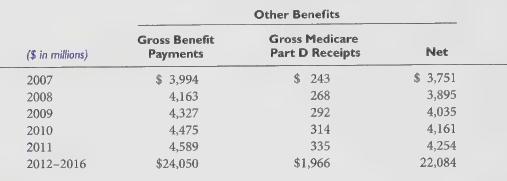
The following benefit payments, which include assumptions related to estimated future employee service, as appropriate, are expected to be paid in the future:
Required:
1. Compute the following OPEB ratios for GM as of December 31, 2006:
a. Short-term OPEB risk ratio (quick).
b. Short-term OPEB risk ratio (extended).
c. Long-term OPEB risk ratio.
2. Explain how the increase in pension benefits of \($4.3\) billion and the decrease to OPEB benefits of \($22\) billion resulting from the 2007 UAW contract will affect GM’s future balance sheets and income statements.
3. Give possible reasons for GM to enter into the 2007 contract with the UAW.
4. Give possible reasons for the UAW to enter into the 2007 contract with GM.
Step by Step Answer:






