The Coca-Cola Company is a global soft drink beverage company (ticker: KO) that is a primary and
Question:
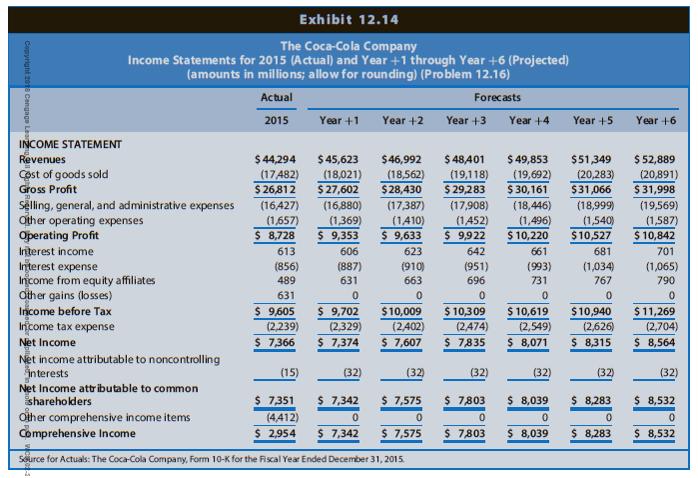
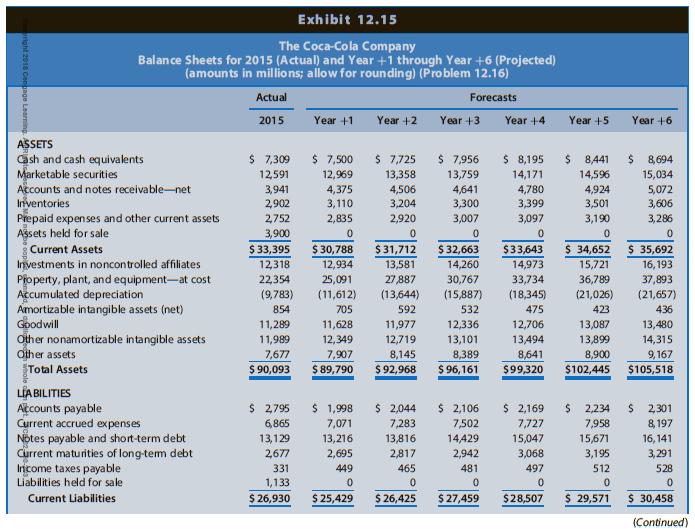
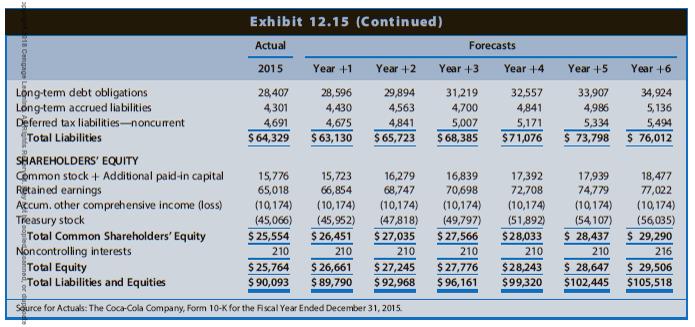
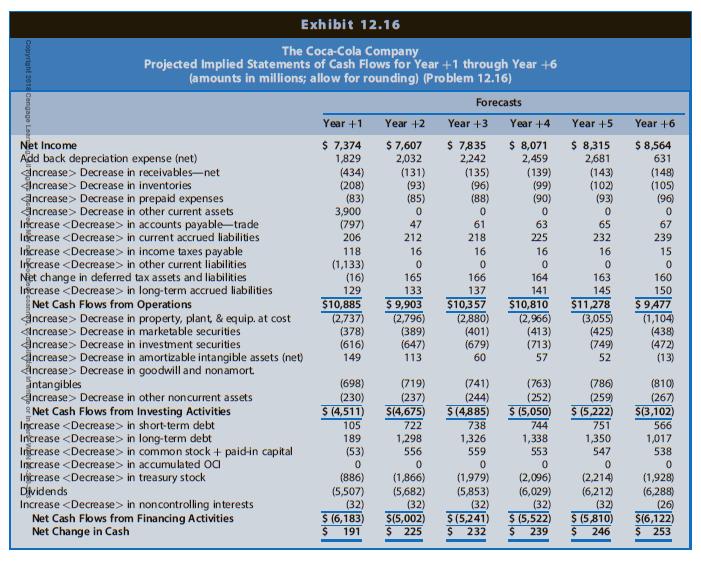
The Coca-Cola Company is a global soft drink beverage company (ticker: KO) that is a primary and direct competitor with Starbucks. The data in Chapter 12’s Exhibits 12.14, 12.15, and 12.16 include the actual amounts for 2013, 2014, and 2015 and projected amounts for Year +1 to Year +6 for the income statements, balance sheets, and statements of cash flows, respectively, for Coca-Cola. The market equity beta for Coca-Cola at the end of 2015 is 0.75. Assume that the risk-free interest rate is 3.0% and the market risk premium is 6.0%. Coca-Cola had 4,324 million shares outstanding at the end of 2015, when Coca-Cola’s share price was $42.96.
REQUIRED
Part I—Computing Coca-Cola’s Share Value Using the Residual Income Valuation Approach
a. Use the CAPM to compute the required rate of return on common equity capital for Coca-Cola.
b. Derive the projected residual income for Coca-Cola for Years +1 through +6 based on the projected financial statements. The financial statement forecasts for Year +6 assume that Coca-Cola will experience a steady-state, long-run growth rate of 3% in Year +6 and beyond.
c. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate, compute the sum of the present value of residual income for Coca-Cola for Years +1 through +5.
d. Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate and the long-run growth rate from Requirement b, compute the continuing value of Coca-Cola as of the start of Year þ6 based on Coca-Cola’s continuing residual income in Year +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value as of the start of Year +6, discount it to present value at the start of Year +1.
e. Compute the value of a share of Coca-Cola common stock.
(1) Compute the total sum of the present value of all residual income (from Requirements c and d).
(2) Add the book value of equity as of the beginning of the valuation (that is, as of the end of 2015, or the start of Year +1).
(3) Adjust the total sum of the present value of residual income plus book value of common equity using the midyear discounting adjustment factor.
(4) Compute the per-share value estimate.
Exhibits 12.14, 12.15, and 12.16
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Reporting Financial Statement Analysis And Valuation A Strategic Perspective
ISBN: 1711
9th Edition
Authors: James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw





