By Newtons universal law of gravitation the free-fall acceleration a of a body, such as the satellite
Question:
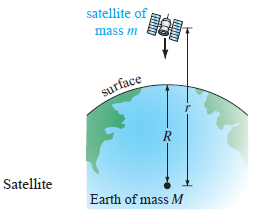
By Newton’s universal law of gravitation the free-fall acceleration a of a body, such as the satellite shown in th4e following figure, falling a great distance to the surface is not the constant g. Rather, the acceleration a is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the center of the Earth, a = k/r2, where k is the constant of proportionality. Use the fact that at the surface of the Earth r = R and a = g to determine k. If the positive direction is upward, use Newton’s second law and his universal law of gravitation to find a differential equation for the distance r.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

A First Course in Differential Equations with Modeling Applications
ISBN: 978-1305965720
11th edition
Authors: Dennis G. Zill
Question Posted:





