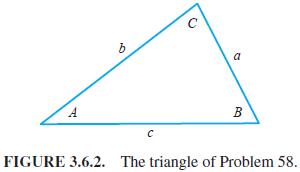
Question: Figure 3.6.2 shows an acute triangle with angles A, B, and C and opposite sides a, b, and c. By dropping a perpendicular from each
Figure 3.6.2 shows an acute triangle with angles A, B, and C and opposite sides a, b, and c. By dropping a perpendicular from each vertex to the opposite side, derive the equations
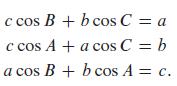
Regarding these as linear equations in the unknowns cosA, cosB, and cosC, use Cramer’s rule to derive the law of cosines by solving for
![]()
Thus
a2 = b2 + c2 - 2bc cosA.
Note that the case A = π/2 (90°) reduces to the Pythagorean theorem.
c cos B + bcos C = a c cos A + a cos C = b a cos B + bcos A = c.
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The coefficient determinant of the line... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


