Based on Exhibit 1, the loss given default for Bond II is: A. Less than that for
Question:
Based on Exhibit 1, the loss given default for Bond II is:
A. Less than that for Bond I.
B. The same as that for Bond I.
C. Greater than that for Bond I.
Lena Liecken is a senior bond analyst at Taurus Investment Management. Kristel Kreming, a junior analyst, works for Liecken in helping conduct fixed-income research for the firm’s portfolio managers. Liecken and Kreming meet to discuss several bond positions held in the firm’s portfolios.
Bonds I and II both have a maturity of one year, an annual coupon rate of 5%, and a market price equal to par value. The risk-free rate is 3%. Historical default experiences of bonds comparable to Bonds I and II are presented in Exhibit 1.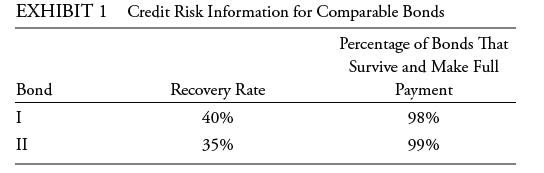
Bond III is a zero-coupon bond with three years to maturity. Liecken evaluates similar bonds and estimates a recovery rate of 38% and a risk-neutral default probability of 2%, assuming conditional probabilities of default. Kreming creates Exhibit 2 to compute Bond III’s credit valuation adjustment. She assumes a flat yield curve at 3%, with exposure, recovery, and loss given default values expressed per 100 of par value.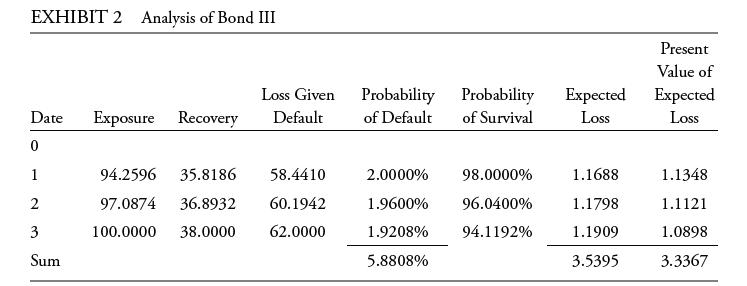
Bond IV is an AA rated bond that matures in five years, has a coupon rate of 6%, and a modified duration of 4.2. Liecken is concerned about whether this bond will be downgraded to an A rating, but she does not expect the bond to default during the next year. Kreming constructs a partial transition matrix, which is presented in Exhibit 3, and suggests using a model to predict the rating change of Bond IV using leverage ratios, return on assets, and macroeconomic variables.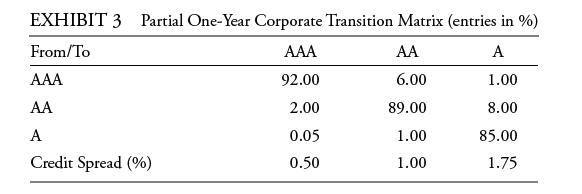
Kreming calculates the risk-neutral probabilities, compares them with the actual default probabilities of bonds evaluated over the past 10 years, and observes that the actual and risk-neutral probabilities differ. She makes two observations regarding the comparison of these probabilities:
• Observation 1: Actual default probabilities include the default risk premium associated with the uncertainty in the timing of the possible default loss.
• Observation 2: The observed spread over the yield on a risk-free bond in practice includes liquidity and tax considerations, in addition to credit risk.
Step by Step Answer:






