Daniela Ibarra is a senior analyst in the fixed-income department of a large wealth management firm. Marten
Question:
Daniela Ibarra is a senior analyst in the fixed-income department of a large wealth management firm. Marten Koning is a junior analyst in the same department, and David Lok is a member of the credit research team.
The firm invests in a variety of bonds. Ibarra is presently analyzing a set of bonds with some similar characteristics, such as four years until maturity and a par value of €1,000. Exhibit 1 includes details of these bonds.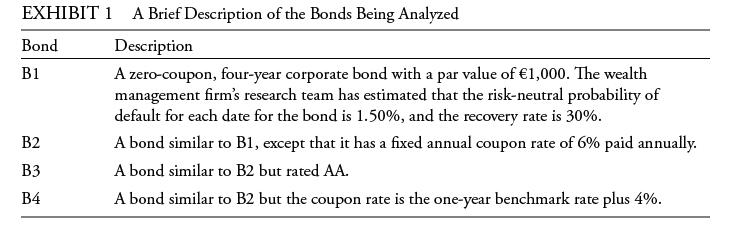
Ibarra asks Koning to assist her with analyzing the bonds. She wants him to perform the analysis with the assumptions that there is no interest rate volatility and that the government bond yield curve is flat at 3%.
Ibarra performs the analysis assuming an upward-sloping yield curve and volatile interest rates. Exhibit 2 provides the data on annual payment benchmark government bonds.
She uses these data to construct a binomial interest rate tree based on an assumption of future interest rate volatility of 20%.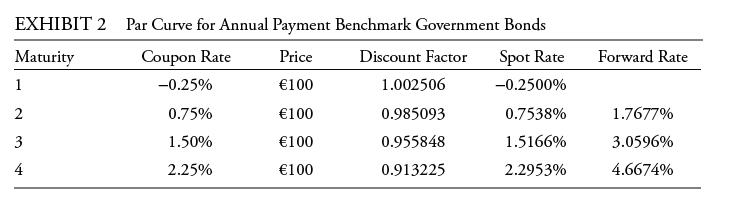
Answer the first five questions (1–5) based on the assumptions made by Marten Koning, the junior analyst. Answer Questions 8–12 based on the assumptions made by Daniela Ibarra, the senior analyst.
All calculations in this problem set are carried out on spreadsheets to preserve precision. The rounded results are reported in the solutions.
In the presentation, Lok is asked why the research team chose to use a reduced-form credit model instead of a structural model. Which statement is he likely to make in reply?
A. Structural models are outdated, having been developed in the 1970s; reduced-form models are more modern, having been developed in the 1990s.
B. Structural models are overly complex because they require the use of option pricing models, whereas reduced-form models use regression analysis.
C. Structural models require “inside” information known to company management, whereas reduced-form models can use publicly available data on the firm.
Step by Step Answer:






