An explosion occurs in the atmosphere when an antiaircraft missile meets its target (Fig. P793). A shock
Question:
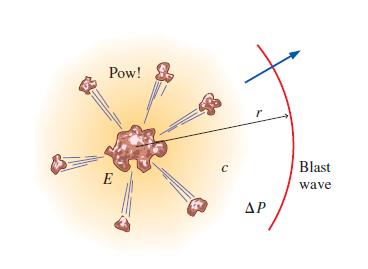
An explosion occurs in the atmosphere when an antiaircraft missile meets its target (Fig. P7–93). A shock wave (also called a blast wave) spreads out radially from the explosion. The pressure difference across the blast wave ΔP and its radial distance r from the center are functions of time t, speed of sound c, and the total amount of energy E released by the explosion.
(a) Generate dimensionless relationships between ΔP and the other parameters and between r and the other parameters.
(b) For a given explosion, if the time t since the explosion doubles, all else being equal, by what factor will ΔP decrease?
FIGURE P7–93
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala
Question Posted:





