In the field of air pollution control, one often needs to sample the quality of a moving
Question:
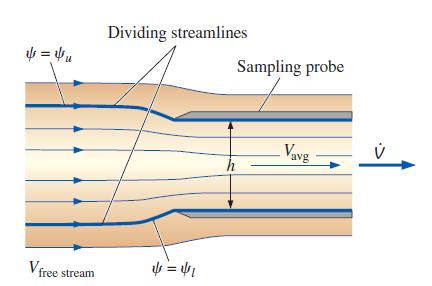
In the field of air pollution control, one often needs to sample the quality of a moving airstream. In such measurements a sampling probe is aligned with the flow as sketched in Fig. P9–52. A suction pump draws air through the probe at volume flow rate V̇ as sketched. For accurate sampling, the air speed through the probe should be the same as that of the airstream (isokinetic sampling). However, if the applied suction is too large, as sketched in Fig. P9–52, the air speed through the probe is greater than that of the airstream (superiso kinetic sampling). For simplicity consider a two-dimensional case in which the sampling probe height is h = 4.58 mm and its width (into the page of Fig. P9–52) is W = 39.5 mm. The values of the stream function corresponding to the lower and upper dividing streamlines are ψ1 = 0.093 m2/s and ψu = 0.150 m2/s, respectively. Calculate the volume flow rate through the probe (in units of m3/s) and the average speed of the air sucked through the probe.
FIGURE P9–52
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala





